"Einstein" redirects here. For other uses, see Einstein (disambiguation).
Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein in 1921
Born 14 March 1879(1879-03-14)
Ulm, Kingdom of Württemberg, German Empire
Died 18 April 1955(1955-04-18) (aged 76)
Princeton, New Jersey, United States
Residence Germany, Italy, Switzerland, United States
Citizenship Württemberg/Germany (until 1896)
Stateless (1896–1901)
Switzerland (from 1901)
Austria (1911–12)
Germany (1914–33)
United States (from 1940)[1]
Alma mater ETH Zurich
University of Zurich
Known for General relativity and special relativity
Photoelectric effect
Mass-energy equivalence
Quantification of the Brownian motion
Einstein field equations
Bose–Einstein statistics
Unified Field Theory
Spouse Mileva Marić (1903–1919)
Elsa Löwenthal, née Einstein, (1919–1936)
Awards Nobel Prize in Physics (1921)
Copley Medal (1925)
Max Planck Medal (1929)
Time Person of the Century
Signature
Albert Einstein ( /ˈælbərt ˈaɪnstaɪn/; German: [ˈalbɐt ˈaɪnʃtaɪn] ( listen); 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist who discovered the theory of general relativity, effecting a revolution in physics. For this achievement, Einstein is often regarded as the father of modern physics.[2] He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect".[3]
Near the beginning of his career, Einstein thought that Newtonian mechanics was no longer enough to reconcile the laws of classical mechanics with the laws of the electromagnetic field. This led to the development of his special theory of relativity. He realized, however, that the principle of relativity could also be extended to gravitational fields, and with his subsequent theory of gravitation in 1916, he published a paper on the general theory of relativity. He continued to deal with problems of statistical mechanics and quantum theory, which led to his explanations of particle theory and the motion of molecules. He also investigated the thermal properties of light which laid the foundation of the photon theory of light. In 1917, Einstein applied the general theory of relativity to model the structure of the universe as a whole.[4]
He was visiting the United States when Hitler came to power in 1933, and did not go back to Germany, where he had been a professor at the Berlin Academy of Sciences. He settled in the U.S., becoming a citizen in 1940. On the eve of World War II, he helped alert President Franklin D. Roosevelt that Germany might be developing an atomic weapon, and recommended that the U.S. begin similar research. Later, together with Bertrand Russell, Einstein signed the Russell–Einstein Manifesto, which highlighted the danger of nuclear weapons. Einstein taught physics at the Institute for Advanced Study at Princeton, New Jersey, until his death in 1955.
Einstein published more than 300 scientific papers along with over 150 non-scientific works.[4][5] His great intelligence and originality have made the word "Einstein" synonymous with genius.[6]
Contents
1 Biography
1.1 Early life and education
1.2 Marriages and children
1.3 Patent office
1.4 Academic career
1.5 Travels abroad
1.6 Emigration from Germany
1.6.1 World War II and the Manhattan Project
1.6.2 U.S. citizenship
1.7 Death
2 Scientific career
2.1 Annus Mirabilis papers
2.2 Thermodynamic fluctuations and statistical physics
2.3 General principles postulated by Einstein
2.4 Theory of relativity and E = mc2
2.5 Photons
2.6 Quantized atomic vibrations
2.7 Adiabatic principle and action-angle variables
2.8 Wave-particle duality
2.9 Theory of critical opalescence
2.10 Zero-point energy
2.11 General relativity and the Equivalence Principle
2.12 Hole argument and Entwurf theory
2.13 Cosmology
2.14 Modern quantum theory
2.15 Bose–Einstein statistics
2.16 Energy momentum pseudotensor
2.17 Unified field theory
2.18 Wormholes
2.19 Einstein–Cartan theory
2.20 Equations of motion
2.21 Einstein's controversial beliefs in physics
2.22 Collaboration with other scientists
2.22.1 Einstein-de Haas experiment
2.22.2 Schrödinger gas model
2.22.3 Einstein refrigerator
2.23 Bohr versus Einstein
2.24 Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen paradox
3 Political and religious views
4 Non-scientific legacy
5 In popular culture
6 Awards and honors
6.1 Awards named after Einstein
7 See also
8 Publications
9 Notes
10 References
11 Further reading
12 External links
Biography
Early life and education
Einstein at the age of 4
Albert Einstein in 1893 (age 14)Albert Einstein was born in Ulm, in the Kingdom of Württemberg in the German Empire on 14 March 1879.[7] His father was Hermann Einstein, a salesman and engineer. His mother was Pauline Einstein (née Koch). In 1880, the family moved to Munich, where his father and his uncle founded Elektrotechnische Fabrik J. Einstein & Cie, a company that manufactured electrical equipment based on direct current.[7]
The Einsteins were non-observant Jews. Albert attended a Catholic elementary school from the age of five for three years. Later, at the age of eight, Einstein was transferred to the Luitpold Gymnasium where he received advanced primary and secondary school education till he left Germany seven years later.[8] Although it has been thought that Einstein had early speech difficulties, this is disputed by the Albert Einstein Archives, and he excelled at the first school that he attended.[9]
His father once showed him a pocket compass; Einstein realized that there must be something causing the needle to move, despite the apparent "empty space".[10] As he grew, Einstein built models and mechanical devices for fun and began to show a talent for mathematics.[7] In 1889, Max Talmud (later changed to Max Talmey) introduced the ten-year old Einstein to key texts in science, mathematics and philosophy, including Immanuel Kant's Critique of Pure Reason and Euclid's Elements (which Einstein called the "holy little geometry book").[11] Talmud was a poor Jewish medical student from Poland. The Jewish community arranged for Talmud to take meals with the Einsteins each week on Thursdays for six years. During this time Talmud wholeheartedly guided Einstein through many secular educational interests.[fn 1][fn 2]
In 1894, his father's company failed: direct current (DC) lost the War of Currents to alternating current (AC). In search of business, the Einstein family moved to Italy, first to Milan and then, a few months later, to Pavia. When the family moved to Pavia, Einstein stayed in Munich to finish his studies at the Luitpold Gymnasium. His father intended for him to pursue electrical engineering, but Einstein clashed with authorities and resented the school's regimen and teaching method. He later wrote that the spirit of learning and creative thought were lost in strict rote learning. In the spring of 1895, he withdrew to join his family in Pavia, convincing the school to let him go by using a doctor's note.[7] During this time, Einstein wrote his first scientific work, "The Investigation of the State of Aether in Magnetic Fields".[14]
Einstein applied directly to the Eidgenössische Polytechnische Schule (ETH) in Zurich, Switzerland. Lacking the requisite Matura certificate, he took an entrance examination, which he failed, although he got exceptional marks in mathematics and physics.[15] The Einsteins sent Albert to Aarau, in northern Switzerland to finish secondary school.[7] While lodging with the family of Professor Jost Winteler, he fell in love with Winteler's daughter, Marie. (His sister Maja later married the Wintelers' son, Paul.)[16] In Aarau, Einstein studied Maxwell's electromagnetic theory. At age 17, he graduated, and, with his father's approval, renounced his citizenship in the German Kingdom of Württemberg to avoid military service, and in 1896 he enrolled in the four year mathematics and physics teaching diploma program at the Polytechnic in Zurich. Marie Winteler moved to Olsberg, Switzerland for a teaching post.
Einstein's future wife, Mileva Marić, also enrolled at the Polytechnic that same year, the only woman among the six students in the mathematics and physics section of the teaching diploma course. Over the next few years, Einstein and Marić's friendship developed into romance, and they read books together on extra-curricular physics in which Einstein was taking an increasing interest. In 1900 Einstein was awarded the Zurich Polytechnic teaching diploma, but Marić failed the examination with a poor grade in the mathematics component, theory of functions.[17] There have been claims that Marić collaborated with Einstein on his celebrated 1905 papers,[18][19] but historians of physics who have studied the issue find no evidence that she made any substantive contributions.[20][21][22][23]
Marriages and children
It has been suggested that Lieserl Einstein be merged into this article or section. (Discuss)
In early 1902, Einstein and Mileva Marić had a daughter they named Lieserl in their correspondence, who was born in Novi Sad where Marić's parents lived.[24] Her full name is not known, and her fate is uncertain after 1903.[25]
Einstein and Marić married in January 1903. In May 1904, the couple's first son, Hans Albert Einstein, was born in Bern, Switzerland. Their second son, Eduard, was born in Zurich in July 1910. In 1914, Einstein moved to Berlin, while his wife remained in Zurich with their sons. Marić and Einstein divorced on 14 February 1919, having lived apart for five years.
Einstein married Elsa Löwenthal (née Einstein) on 2 June 1919, after having had a relationship with her since 1912. She was his first cousin maternally and his second cousin paternally. In 1933, they emigrated permanently to the United States. In 1935, Elsa Einstein was diagnosed with heart and kidney problems and died in December 1936.[26]
Patent office
Left to right: Conrad Habicht, Maurice Solovine and Einstein, who founded the Olympia Academy
Einstein's home in BernAfter graduating, Einstein spent almost two frustrating years searching for a teaching post, but a former classmate's father helped him secure a job in Bern, at the Federal Office for Intellectual Property, the patent office, as an assistant examiner.[27] He evaluated patent applications for electromagnetic devices. In 1903, Einstein's position at the Swiss Patent Office became permanent, although he was passed over for promotion until he "fully mastered machine technology".[28]
Much of his work at the patent office related to questions about transmission of electric signals and electrical-mechanical synchronization of time, two technical problems that show up conspicuously in the thought experiments that eventually led Einstein to his radical conclusions about the nature of light and the fundamental connection between space and time.[29]
With a few friends he met in Bern, Einstein started a small discussion group, self-mockingly named "The Olympia Academy", which met regularly to discuss science and philosophy. Their readings included the works of Henri Poincaré, Ernst Mach, and David Hume, which influenced his scientific and philosophical outlook.
Academic career
Einstein's official 1921 portrait after receiving the Nobel Prize in Physics.In 1901, Einstein had a paper on the capillary forces of a straw published in the prestigious Annalen der Physik.[30] On 30 April 1905, he completed his thesis, with Alfred Kleiner, Professor of Experimental Physics, serving as pro-forma advisor. Einstein was awarded a PhD by the University of Zurich. His dissertation was entitled "A New Determination of Molecular Dimensions".[31] That same year, which has been called Einstein's annus mirabilis or "miracle year", he published four groundbreaking papers, on the photoelectric effect, Brownian motion, special relativity, and the equivalence of matter and energy, which were to bring him to the notice of the academic world.
By 1908, he was recognized as a leading scientist, and he was appointed lecturer at the University of Bern. The following year, he quit the patent office and the lectureship to take the position of physics docent[32] at the University of Zurich. He became a full professor at Karl-Ferdinand University in Prague in 1911. In 1914, he returned to Germany after being appointed director of the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Physics (1914–1932)[33] and a professor at the Humboldt University of Berlin, although with a special clause in his contract that freed him from most teaching obligations. He became a member of the Prussian Academy of Sciences. In 1916, Einstein was appointed president of the German Physical Society (1916–1918).[34][35]
In 1911, he had calculated that, based on his new theory of general relativity, light from another star would be bent by the Sun's gravity. That prediction was claimed confirmed by observations made by a British expedition led by Sir Arthur Eddington during the solar eclipse of May 29, 1919. International media reports of this made Einstein world famous. On 7 November 1919, the leading British newspaper The Times printed a banner headline that read: "Revolution in Science – New Theory of the Universe – Newtonian Ideas Overthrown".[36] (Much later, questions were raised whether the measurements were accurate enough to support Einstein's theory.)
In 1921, Einstein was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics. Because relativity was still considered somewhat controversial, it was officially bestowed for his explanation of the photoelectric effect. He also received the Copley Medal from the Royal Society in 1925.
Travels abroad
Einstein visited New York City for the first time on 2 April 1921, where he received an official welcome by the Mayor, followed by three weeks of lectures and receptions. He went on to deliver several lectures at Columbia University and Princeton University, and in Washington he accompanied representatives of the National Academy of Science on a visit to the White House. On his return to Europe he was the guest of the British statesman and philosopher Viscount Haldane in London, where he met several renowned scientific, intellectual and political figures, and delivered a lecture at Kings College.[37]
In 1922, he traveled throughout Asia and later to Palestine, as part of a six-month excursion and speaking tour. His travels included Singapore, Ceylon, and Japan, where he gave a series of lectures to thousands of Japanese. His first lecture in Tokyo lasted four hours, after which he met the emperor and empress at the Imperial Palace where thousands came to watch. Einstein later gave his impressions of the Japanese in a letter to his sons:[38]:307 "Of all the people I have met, I like the Japanese most, as they are modest, intelligent, considerate, and have a feel for art."[38]:308
On his return voyage, he also visited Palestine for 12 days in what would become his only visit to that region. "He was greeted with great British pomp, as if he were a head of state rather than a theoretical physicist", writes Isaacson. This included a cannon salute upon his arrival at the residence of the British high commissioner, Sir Herbert Samuel. During one reception given to him, the building was "stormed by throngs who wanted to hear him". In Einstein's talk to the audience, he expressed his happiness over the event:
I consider this the greatest day of my life. Before, I have always found something to regret in the Jewish soul, and that is the forgetfulness of its own people. Today, I have been made happy by the sight of the Jewish people learning to recognize themselves and to make themselves recognized as a force in the world.[39]:308
Emigration from Germany
Cartoon of Einstein, who has shed his "Pacifism" wings, standing next to a pillar labeled "World Peace." He is rolling up his sleeves and holding a sword labeled "Preparedness." (circa 1933)In 1933, Einstein decided to emigrate to the United States due to the rise to power of the Nazis under Germany's new chancellor, Adolf Hitler.[40] While visiting American universities in April, 1933, he learned that the new German government had passed a law barring Jews from holding any official positions, including teaching at universities. A month later, the Nazi book burnings occurred, with Einstein's works being among those burnt, and Nazi propaganda minister Joseph Goebbels proclaimed, "Jewish intellectualism is dead."[39] Einstein also learned that his name was on a list of assassination targets, with a "$5,000 bounty on his head". One German magazine included him in a list of enemies of the German regime with the phrase, "not yet hanged".[39]
Einstein was undertaking his third two-month visiting professorship at the California Institute of Technology when Hitler came to power in Germany. On his return to Europe in March 1933 he resided in Belgium for some months, before temporarily moving to England.[41]
He took up a position at the Institute for Advanced Study at Princeton, New Jersey,[42] an affiliation that lasted until his death in 1955. There, he tried to develop a unified field theory and to refute the accepted interpretation of quantum physics, both unsuccessfully. He and Kurt Gödel, another Institute member, became close friends. They would take long walks together discussing their work. His last assistant was Bruria Kaufman, who later became a renowned physicist.
Other scientists also fled to America. Among them were Nobel laureates and professors of theoretical physics. With so many other Jewish scientists now forced by circumstances to live in America, often working side by side, Einstein wrote to a friend, "For me the most beautiful thing is to be in contact with a few fine Jews—a few millennia of a civilized past do mean something after all." In another letter he writes, "In my whole life I have never felt so Jewish as now."[39]
World War II and the Manhattan Project
In 1939, a group of Hungarian scientists that included Hungarian emigre physicist Leo Szilard attempted to alert Washington of ongoing Nazi atomic bomb research. The group's warnings were discounted.[43]
In the summer of 1939, a few months before the beginning of World War II in Europe, Einstein was persuaded to lend his prestige by writing a letter, with Leo Szilard, to President Franklin D. Roosevelt, in order to alert him of the possibility that Nazi Germany might be developing an atomic bomb. At the same time, the letter recommended that the U.S. government should pay attention to and become directly involved with uranium research, and associated chain reaction research. Einstein and Szilard, along with other refugees such as Edward Teller and Eugene Wigner, "regarded it as their responsibility to alert Americans to the possibility that German scientists might win the race to build an atomic bomb, and to warn that Hitler would be more than willing to resort to such a weapon."[38]:630 [44]
The letter is believed to be "arguably the key stimulus for the U.S. adoption of serious investigations into nuclear weapons on the eve of the U.S. entry into World War II".[45] President Roosevelt could not take the risk of allowing Hitler to possess atomic bombs first. As a result of Einstein's letter and his meetings with Roosevelt, the U.S. entered the "race" to develop the bomb, drawing on its "immense material, financial, and scientific resources" to initiate the Manhattan Project. It became the only country to develop an atomic bomb during World War II.
For Einstein, "war was a disease . . . [and] he called for resistance to war." But in 1933, after Hitler assumed full power in Germany, "he renounced pacifism altogether . . . In fact, he urged the Western powers to prepare themselves against another German onslaught."[46]:110 In 1954, a year before his death, Einstein said to his old friend, Linus Pauling, "I made one great mistake in my life — when I signed the letter to President Roosevelt recommending that atom bombs be made; but there was some justification — the danger that the Germans would make them..."[47]
U.S. citizenship
Accepting U.S. citizenship, 1940
Einstein with David Ben Gurion, 1951Einstein became an American citizen in 1940. Not long after settling into his career at Princeton, he expressed his appreciation of the "meritocracy" in American culture when compared to Europe. According to Isaacson, he recognized the "right of individuals to say and think what they pleased", without social barriers, and as result, the individual was "encouraged" to be more creative, a trait he valued from his own early education. Einstein writes:
What makes the new arrival devoted to this country is the democratic trait among the people. No one humbles himself before another person or class. . . American youth has the good fortune not to have its outlook troubled by outworn traditions.[39]:432
As a member of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People NAACP at Princeton who campaigned for the civil rights of African Americans, Einstein corresponded with civil rights activist W. E. B. Du Bois, and in 1946 Einstein called racism America's "worst disease".[48] He later stated, "Race prejudice has unfortunately become an American tradition which is uncritically handed down from one generation to the next. The only remedies are enlightenment and education".[49]
After the death of Israel's first president, Chaim Weizmann, in November 1952, Prime Minister David Ben-Gurion offered Einstein the position of President of Israel, a mostly ceremonial post.[50] The offer was presented by Israel's ambassador in Washington, Abba Eban, who explained that the offer "embodies the deepest respect which the Jewish people can repose in any of its sons".[38]:522 However, Einstein declined, and wrote in his response that he was "deeply moved", and "at once saddened and ashamed" that he could not accept it:
All my life I have dealt with objective matters, hence I lack both the natural aptitude and the experience to deal properly with people and to exercise official function. I am the more distressed over these circumstances because my relationship with the Jewish people became my strongest human tie once I achieved complete clarity about our precarious position among the nations of the world.[38]:522 [50][51]
Death
The New York World-Telegram announces Einstein's death on April 18, 1955.On April 17, 1955, Albert Einstein experienced internal bleeding caused by the rupture of an abdominal aortic aneurysm, which had previously been reinforced surgically by Dr. Rudolph Nissen in 1948.[52] He took the draft of a speech he was preparing for a television appearance commemorating the State of Israel's seventh anniversary with him to the hospital, but he did not live long enough to complete it.[53] Einstein refused surgery, saying: "I want to go when I want. It is tasteless to prolong life artificially. I have done my share, it is time to go. I will do it elegantly."[54] He died in Princeton Hospital early the next morning at the age of 76, having continued to work until near the end.
Einstein's remains were cremated and his ashes were scattered at an undisclosed location.[55][56] During the autopsy, the pathologist of Princeton Hospital, Thomas Stoltz Harvey, removed Einstein's brain for preservation, without the permission of his family, in hope that the neuroscience of the future would be able to discover what made Einstein so intelligent.[57] In his lecture at Einstein's memorial, nuclear physicist Robert Oppenheimer summarized his impression of him as a person:[46]
"He was almost wholly without sophistication and wholly without worldliness . . . There was always with him a wonderful purity at once childlike and profoundly stubborn."
Scientific career
Albert Einstein in 1904
The photoelectric effect. Incoming photons on the left strike a metal plate (bottom), and eject electrons, depicted as flying off to the right.Throughout his life, Einstein published hundreds of books and articles.[5][7] In addition to the work he did by himself he also collaborated with other scientists on additional projects including the Bose–Einstein statistics, the Einstein refrigerator and others.[58]
Annus Mirabilis papers
Main articles: Annus Mirabilis papers, Photoelectric effect, Special theory of relativity, and Mass–energy equivalence
The Annus Mirabilis papers are four articles pertaining to the photoelectric effect, Brownian motion, the special theory of relativity, and E = mc2 that Albert Einstein published in the Annalen der Physik scientific journal in 1905. These four works contributed substantially to the foundation of modern physics and changed views on space, time, and matter.
Thermodynamic fluctuations and statistical physics
Main article: statistical physics
Albert Einstein's first paper[59] submitted in 1900 to Annalen der Physik was on capillary attraction. It was published in 1901 titled Folgerungen aus den Capillaritätserscheinungen, which was translated as "Conclusions from the capillarity phenomena". Two papers he published in 1902-1903 (thermodynamics) attempted to interpret phenomena from a statistical atomic point of view. These papers were the foundation for the 1905 paper on Brownian motion. These published calculations (1905) showed that Brownian movement can be construed as firm evidence that molecules exist.
His research in 1903 and 1904 was mainly concerned with the effect of finite atomic size on diffusion phenomena.[59] Einstein's theory of Brownian motion was the first paper in the field of statistical physics.[citation needed] It is the most frequently cited, of the Annus Mirabilis papers.[citation needed]
General principles postulated by Einstein
He articulated the principle of relativity. This was understood by Hermann Minkowski to be a generalization of rotational invariance from space to space-time. Other principles postulated by Einstein and later vindicated are the principle of equivalence and the principle of adiabatic invariance of the quantum number. Another of Einstein's general principles, Mach's principle, is fiercely debated, and whether it holds in our world or not is still not definitively established.[citation needed]
Theory of relativity and E = mc2
Main article: History of special relativity
Einstein's "Zur Elektrodynamik bewegter Körper" ("On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies") was received on June 30, 1905 and published September 26 of that same year. It reconciles Maxwell's equations for electricity and magnetism with the laws of mechanics, by introducing major changes to mechanics close to the speed of light. This later became known as Einstein's special theory of relativity.
Consequences of this include the time-space frame of a moving body slowing down and contracting (in the direction of motion) relative to the frame of the observer. This paper also argued that the idea of a luminiferous aether – one of the leading theoretical entities in physics at the time – was superfluous.[60]
In his paper on mass–energy equivalence, which had previously been considered to be distinct concepts, Einstein deduced from his equations of special relativity what has been called the 20th century's best-known equation: E = mc2.[61][62] This equation suggests that tiny amounts of mass could be converted into huge amounts of energy and presaged the development of nuclear power.[63] Einstein's 1905 work on relativity remained controversial for many years, but was accepted by leading physicists, starting with Max Planck.[64][65]
Photons
Main article: Photon
In a 1905 paper,[66] Einstein postulated that light itself consists of localized particles (quanta). Einstein's light quanta were nearly universally rejected by all physicists, including Max Planck and Niels Bohr. This idea only became universally accepted in 1919, with Robert Millikan's detailed experiments on the photoelectric effect, and with the measurement of Compton scattering.
Einstein concluded that each wave of frequency f is associated with a collection of photons with energy hf each, where h is Planck's constant. He does not say much more, because he is not sure how the particles are related to the wave. But he does suggest that this idea would explain certain experimental results, notably the photoelectric effect.[67]
Quantized atomic vibrations
Main article: Einstein solid
In 1907 Einstein proposed a model of matter where each atom in a lattice structure is an independent harmonic oscillator. In the Einstein model, each atom oscillates independently - a series of equally spaced quantized states for each oscillator. Einstein was aware that getting the frequency of the actual oscillations would be different, but he nevertheless proposed this theory because it was a particularly clear demonstration that quantum mechanics could solve the specific heat problem in classical mechanics. Peter Debye refined this model.[68]
This work was the foundation of condensed matter physics.[citation needed]
Adiabatic principle and action-angle variables
Main article: Old quantum theory
Throughout the 1910s, quantum mechanics expanded in scope to cover many different systems. After Ernest Rutherford discovered the nucleus and proposed that electrons orbit like planets, Niels Bohr was able to show that the same quantum mechanical postulates introduced by Planck and developed by Einstein would explain the discrete motion of electrons in atoms, and the periodic table of the elements.
Einstein contributed to these developments by linking them with the 1898 arguments Wilhelm Wien had made. Wien had shown that the hypothesis of adiabatic invariance of a thermal equilibrium state allows all the blackbody curves at different temperature to be derived from one another by a simple shifting process. Einstein noted in 1911 that the same adiabatic principle shows that the quantity which is quantized in any mechanical motion must be an adiabatic invariant. Arnold Sommerfeld identified this adiabatic invariant as the action variable of classical mechanics. The law that the action variable is quantized was a basic principle of the quantum theory as it was known between 1900 and 1925.[citation needed]
Wave-particle duality
Main article: Wave-particle duality
Although the patent office promoted Einstein to Technical Examiner Second Class in 1906, he had not given up on academia. In 1908, he became a privatdozent at the University of Bern.[69] In "über die Entwicklung unserer Anschauungen über das Wesen und die Konstitution der Strahlung" ("The Development of Our Views on the Composition and Essence of Radiation"), on the quantization of light, and in an earlier 1909 paper, Einstein showed that Max Planck's energy quanta must have well-defined momenta and act in some respects as independent, point-like particles. This paper introduced the photon concept (although the name photon was introduced later by Gilbert N. Lewis in 1926) and inspired the notion of wave-particle duality in quantum mechanics.
Theory of critical opalescence
Main article: Critical opalescence
Einstein returned to the problem of thermodynamic fluctuations, giving a treatment of the density variations in a fluid at its critical point. Ordinarily the density fluctuations are controlled by the second derivative of the free energy with respect to the density. At the critical point, this derivative is zero, leading to large fluctuations. The effect of density fluctuations is that light of all wavelengths is scattered, making the fluid look milky white. Einstein relates this to Raleigh scattering, which is what happens when the fluctuation size is much smaller than the wavelength, and which explains why the sky is blue.[70] Einstein quantitatively derived critical opalescence from a treatment of density fluctuations, and demonstrated how both the effect and Rayleigh scattering originate from the atomistic constitution of matter.
Einstein at the Solvay Conference in 1911Zero-point energy
Main article: Zero-point energy
Einstein's physical intuition led him to note that Planck's oscillator energies had an incorrect zero point. He modified Planck's hypothesis by stating that the lowest energy state of an oscillator is equal to 1⁄2hf, to half the energy spacing between levels. This argument, which was made in 1913 in collaboration with Otto Stern, was based on the thermodynamics of a diatomic molecule which can split apart into two free atoms.
General relativity and the Equivalence Principle
Main article: History of general relativity
See also: Principle of equivalence and Theory of relativity
General relativity (GR) is a theory of gravitation that was developed by Albert Einstein between 1907 and 1915. According to general relativity, the observed gravitational attraction between masses results from the warping of space and time by those masses. General relativity has developed into an essential tool in modern astrophysics. It provides the foundation for the current understanding of black holes, regions of space where gravitational attraction is so strong that not even light can escape.
As Albert Einstein later said, the reason for the development of general relativity was that the preference of inertial motions within special relativity was unsatisfactory, while a theory which from the outset prefers no state of motion (even accelerated ones) should appear more satisfactory.[71] So in 1908 he published an article on acceleration under special relativity. In that article, he argued that free fall is really inertial motion, and that for a freefalling observer the rules of special relativity must apply. This argument is called the Equivalence principle. In the same article, Einstein also predicted the phenomenon of gravitational time dilation. In 1911, Einstein published another article expanding on the 1907 article, in which additional effects such as the deflection of light by massive bodies were predicted.
Hole argument and Entwurf theory
Main article: Hole argument
While developing general relativity, Einstein became confused about the gauge invariance in the theory. He formulated an argument that led him to conclude that a general relativistic field theory is impossible. He gave up looking for fully generally covariant tensor equations, and searched for equations that would be invariant under general linear transformations only.
In June, 1913 the Entwurf ("draft") theory was the result of these investigations. As its name suggests, it was a sketch of a theory, with the equations of motion supplemented by additional gauge fixing conditions. Simultaneously less elegant and more difficult than general relativity, after more than two years of intensive work Einstein abandoned the theory in November, 1915 after realizing that the hole argument was mistaken.[72]
Cosmology
Main article: Cosmology
In 1917, Einstein applied the General theory of relativity to model the structure of the universe as a whole. He wanted the universe to be eternal and unchanging, but this type of universe is not consistent with relativity. To fix this, Einstein modified the general theory by introducing a new notion, the cosmological constant. With a positive cosmological constant, the universe could be an eternal static sphere[73]
Einstein believed a spherical static universe is philosophically preferred, because it would obey Mach's principle. He had shown that general relativity incorporates Mach's principle to a certain extent in frame dragging by gravitomagnetic fields, but he knew that Mach's idea would not work if space goes on forever. In a closed universe, he believed that Mach's principle would hold.
Mach's principle has generated much controversy over the years.
Einstein in his office at the University of Berlin.Modern quantum theory
Main article: Schrödinger equation
In 1917, at the height of his work on relativity, Einstein published an article in Physikalische Zeitschrift that proposed the possibility of stimulated emission, the physical process that makes possible the maser and the laser.[74] This article showed that the statistics of absorption and emission of light would only be consistent with Planck's distribution law if the emission of light into a mode with n photons would be enhanced statistically compared to the emission of light into an empty mode. This paper was enormously influential in the later development of quantum mechanics, because it was the first paper to show that the statistics of atomic transitions had simple laws. Einstein discovered Louis de Broglie's work, and supported his ideas, which were received skeptically at first. In another major paper from this era, Einstein gave a wave equation for de Broglie waves, which Einstein suggested was the Hamilton–Jacobi equation of mechanics. This paper would inspire Schrödinger's work of 1926.
Bose–Einstein statistics
Main article: Bose–Einstein condensation
In 1924, Einstein received a description of a statistical model from Indian physicist Satyendra Nath Bose, based on a counting method that assumed that light could be understood as a gas of indistinguishable particles. Einstein noted that Bose's statistics applied to some atoms as well as to the proposed light particles, and submitted his translation of Bose's paper to the Zeitschrift für Physik. Einstein also published his own articles describing the model and its implications, among them the Bose–Einstein condensate phenomenon that some particulates should appear at very low temperatures.[75] It was not until 1995 that the first such condensate was produced experimentally by Eric Allin Cornell and Carl Wieman using ultra-cooling equipment built at the NIST–JILA laboratory at the University of Colorado at Boulder.[76] Bose–Einstein statistics are now used to describe the behaviors of any assembly of bosons. Einstein's sketches for this project may be seen in the Einstein Archive in the library of the Leiden University.[58]
Energy momentum pseudotensor
Main article: Stress-energy-momentum pseudotensor
General relativity includes a dynamical spacetime, so it is difficult to see how to identify the conserved energy and momentum. Noether's theorem allows these quantities to be determined from a Lagrangian with translation invariance, but general covariance makes translation invariance into something of a gauge symmetry. The energy and momentum derived within general relativity by Noether's presecriptions do not make a real tensor for this reason.
Einstein argued that this is true for fundamental reasons, because the gravitational field could be made to vanish by a choice of coordinates. He maintained that the non-covariant energy momentum pseudotensor was in fact the best description of the energy momentum distribution in a gravitational field. This approach has been echoed by Lev Landau and Evgeny Lifshitz, and others, and has become standard.
The use of non-covariant objects like pseudotensors was heavily criticized in 1917 by Erwin Schrödinger and others.
Unified field theory
Main article: Classical unified field theories
Following his research on general relativity, Einstein entered into a series of attempts to generalize his geometric theory of gravitation to include electromagnetism as another aspect of a single entity. In 1950, he described his "unified field theory" in a Scientific American article entitled "On the Generalized Theory of Gravitation".[77] Although he continued to be lauded for his work, Einstein became increasingly isolated in his research, and his efforts were ultimately unsuccessful. In his pursuit of a unification of the fundamental forces, Einstein ignored some mainstream developments in physics, most notably the strong and weak nuclear forces, which were not well understood until many years after his death. Mainstream physics, in turn, largely ignored Einstein's approaches to unification. Einstein's dream of unifying other laws of physics with gravity motivates modern quests for a theory of everything and in particular string theory, where geometrical fields emerge in a unified quantum-mechanical setting.
Wormholes
Main article: Wormhole
Einstein collaborated with others to produce a model of a wormhole. His motivation was to model elementary particles with charge as a solution of gravitational field equations, in line with the program outlined in the paper "Do Gravitational Fields play an Important Role in the Constitution of the Elementary Particles?". These solutions cut and pasted Schwarzschild black holes to make a bridge between two patches.
If one end of a wormhole was positively charged, the other end would be negatively charged. These properties led Einstein to believe that pairs of particles and antiparticles could be described in this way.
Einstein–Cartan theory
Main article: Einstein–Cartan theory
In order to incorporate spinning point particles into general relativity, the affine connection needed to be generalized to include an antisymmetric part, called the torsion. This modification was made by Einstein and Cartan in the 1920s.
Equations of motion
Main article: Einstein–Infeld–Hoffmann equations
The theory of general relativity has a fundamental law – the Einstein equations which describe how space curves, the geodesic equation which describes how particles move may be derived from the Einstein equations.
Since the equations of general relativity are non-linear, a lump of energy made out of pure gravitational fields, like a black hole, would move on a trajectory which is determined by the Einstein equations themselves, not by a new law. So Einstein proposed that the path of a singular solution, like a black hole, would be determined to be a geodesic from general relativity itself.
This was established by Einstein, Infeld, and Hoffmann for pointlike objects without angular momentum, and by Roy Kerr for spinning objects.
Einstein's controversial beliefs in physics
In addition to his well-accepted results, some of Einstein's views are regarded as controversial:
In the special relativity paper (in 1905), Einstein noted that, given a specific definition of the word "force" (a definition which he later agreed was not advantageous), and if we choose to maintain (by convention) the equation mass x acceleration = force, then one arrives at as the expression for the transverse mass of a fast moving particle. This differs from the accepted expression today, because, as noted in the footnotes to Einstein's paper added in the 1913 reprint, "it is more to the point to define force in such a way that the laws of energy and momentum assume the simplest form", as was done, for example, by Max Planck in 1906, who gave the now familiar expression for the transverse mass. As Miller points out, this is equivalent to the transverse mass predictions of both Einstein and Lorentz. Einstein had commented already in the 1905 paper that "With a different definition of force and acceleration, we should naturally obtain other expressions for the masses. This shows that in comparing different theories... we must proceed very cautiously."[78]
Einstein published (in 1922) a qualitative theory of superconductivity based on the vague idea of electrons shared in orbits. This paper predated modern quantum mechanics, and today is regarded as being incorrect. The current theory of low temperature superconductivity was only worked out in 1957, thirty years after the establishing of modern quantum mechanics. However, even today, superconductivity is not well understood, and alternative theories continue to be put forward, especially to account for high-temperature superconductors.[citation needed]
After introducing the concept of gravitational waves in 1917, Einstein subsequently entertained doubts about whether they could be physically realized. In 1937 he published a paper saying that the focusing properties of geodesics in general relativity would lead to an instability which causes plane gravitational waves to collapse in on themselves. While this is true to a certain extent in some limits, because gravitational instabilities can lead to a concentration of energy density into black holes, for plane waves of the type Einstein and Rosen considered in their paper, the instabilities are under control. Einstein retracted this position a short time later.[citation needed]
Einstein denied several times that black holes could form. In 1939 he published a paper that argues that a star collapsing would spin faster and faster, spinning at the speed of light with infinite energy well before the point where it is about to collapse into a black hole. This paper received no citations, and the conclusions are well understood to be wrong. Einstein's argument itself is inconclusive, since he only shows that stable spinning objects have to spin faster and faster to stay stable before the point where they collapse. But it is well understood today (and was understood well by some even then) that collapse cannot happen through stationary states the way Einstein imagined. Nevertheless, the extent to which the models of black holes in classical general relativity correspond to physical reality remains unclear, and in particular the implications of the central singularity implicit in these models are still not understood. Efforts to conclusively prove the existence of event horizons have still not been successful.[citation needed]
Closely related to his rejection of black holes, Einstein believed that the exclusion of singularities might restrict the class of solutions of the field equations so as to force solutions compatible with quantum mechanics, but no such theory has ever been found.[citation needed]
In the early days of quantum mechanics, Einstein tried to show that the uncertainty principle was not valid, but by 1927 he had become convinced that it was valid.[citation needed]
In the EPR paper, Einstein argued that quantum mechanics cannot be a complete realistic and local representation of phenomena, given specific definitions of "realism", "locality", and "completeness". The modern consensus is that Einstein's concept of realism is too restrictive.[citation needed]
Einstein himself considered the introduction of the cosmological term in his 1917 paper founding cosmology as a "blunder".[79] The theory of general relativity predicted an expanding or contracting universe, but Einstein wanted a universe which is an unchanging three dimensional sphere, like the surface of a three dimensional ball in four dimensions. He wanted this for philosophical reasons, so as to incorporate Mach's principle in a reasonable way. He stabilized his solution by introducing a cosmological constant, and when the universe was shown to be expanding, he retracted the constant as a blunder. This is not really much of a blunder – the cosmological constant is necessary within general relativity as it is currently understood, and it is widely believed to have a nonzero value today.
Einstein did not immediately appreciate the value of Minkowski's four-dimensional formulation of special relativity, although within a few years he had adopted it as the basis for his theory of gravitation.[citation needed]
Finding it too formal, Einstein believed that Heisenberg's matrix mechanics was incorrect. He changed his mind when Schrödinger and others demonstrated that the formulation in terms of the Schrödinger equation, based on Einstein's wave-particle duality was equivalent to Heisenberg's matrices.[citation needed]
Collaboration with other scientists
In addition to long time collaborators Leopold Infeld, Nathan Rosen, Peter Bergmann and others, Einstein also had some one-shot collaborations with various scientists.
Einstein-de Haas experiment
Main article: Einstein-de Haas effect
Einstein and De Haas demonstrated that magnetization is due to the motion of electrons, nowadays known to be the spin. In order to show this, they reversed the magnetization in an iron bar suspended on a torsion pendulum. They confirmed that this leads the bar to rotate, because the electron's angular momentum changes as the magnetization changes. This experiment needed to be sensitive, because the angular momentum associated with electrons is small, but it definitively established that electron motion of some kind is responsible for magnetization.
Schrödinger gas model
Einstein suggested to Erwin Schrödinger that he might be able to reproduce the statistics of a Bose–Einstein gas by considering a box. Then to each possible quantum motion of a particle in a box associate an independent harmonic oscillator. Quantizing these oscillators, each level will have an integer occupation number, which will be the number of particles in it.
This formulation is a form of second quantization, but it predates modern quantum mechanics. Erwin Schrödinger applied this to derive the thermodynamic properties of a semiclassical[disambiguation needed] ideal gas. Schrödinger urged Einstein to add his name as co-author, although Einstein declined the invitation.[80]
Einstein refrigerator
Main article: Einstein refrigerator
In 1926, Einstein and his former student Leó Szilárd co-invented (and in 1930, patented) the Einstein refrigerator. This absorption refrigerator was then revolutionary for having no moving parts and using only heat as an input.[81] On 11 November 1930, U.S. Patent 1,781,541 was awarded to Albert Einstein and Leó Szilárd for the refrigerator. Their invention was not immediately put into commercial production, as the most promising of their patents were quickly bought up by the Swedish company Electrolux to protect its refrigeration technology from competition.[82]
Bohr versus Einstein
Main article: Bohr–Einstein debates
Einstein and Niels Bohr, 1925In the 1920s, quantum mechanics developed into a more complete theory. Einstein was unhappy with the Copenhagen interpretation of quantum theory developed by Niels Bohr and Werner Heisenberg, both in its outcomes and its instrumentalist methodology, Einstein being a scientific realist. In this interpretation, quantum phenomena are inherently probabilistic, with definite states resulting only upon interaction with classical systems. A public debate between Einstein and Bohr followed, lasting on and off for many years (including during the Solvay Conferences). Einstein formulated thought experiments against the Copenhagen interpretation, which were all rebutted by Bohr. In a 1926 letter to Max Born, Einstein wrote: "I, at any rate, am convinced that He [God] does not throw dice."[83]
Einstein was never satisfied by what he perceived to be quantum theory's intrinsically incomplete description of nature, and in 1935 he further explored the issue in collaboration with Boris Podolsky and Nathan Rosen, noting that the theory seems to require non-local interactions; this is known as the EPR paradox.[84] The EPR experiment has since been performed, with results confirming quantum theory's predictions.[85] Repercussions of the Einstein–Bohr debate have found their way into philosophical discourse.
Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen paradox
Main article: EPR paradox
In 1935, Einstein returned to the question of quantum mechanics. He considered how a measurement on one of two entangled particles would affect the other. He noted, along with his collaborators, that by performing different measurements on the distant particle, either of position or momentum, different properties of the entangled partner could be discovered without disturbing it in any way.
He then used a hypothesis of local realism to conclude that the other particle had these properties already determined. The principle he proposed is that if it is possible to determine what the answer to a position or momentum measurement would be, without in any way disturbing the particle, then the particle actually has values of position or momentum.
This principle distilled the essence of Einstein's objection to quantum mechanics. As a physical principle, it has since been shown to be incompatible with experiments.
Political and religious views
Main articles: Albert Einstein's political views and Albert Einstein's religious views
Albert Einstein, seen here with his wife Elsa Einstein and Zionist leaders, including future President of Israel Chaim Weizmann, his wife Dr. Vera Weizmann, Menahem Ussishkin, and Ben-Zion Mossinson on arrival in New York City in 1921.Albert Einstein's political views emerged publicly in the middle of the 20th century due to his fame and reputation for genius. Einstein offered to and was called on to give judgments and opinions on matters often unrelated to theoretical physics or mathematics. (see main article)
Einstein's views on religious belief have been collected from interviews and original writings. These views covered theological determinism, agnosticism, humanism along with ethical culture, opting for Spinoza's god over belief in a personal god, religious belief, enlightenment and liberation, Jews, Christianity, Jesus, Pope Pius XII, and the Catholic Church. (see main article)
Non-scientific legacy
While travelling, Einstein wrote daily to his wife Elsa and adopted stepdaughters Margot and Ilse. The letters were included in the papers bequeathed to The Hebrew University. Margot Einstein permitted the personal letters to be made available to the public, but requested that it not be done until twenty years after her death (she died in 1986[86]). Barbara Wolff, of The Hebrew University's Albert Einstein Archives, told the BBC that there are about 3,500 pages of private correspondence written between 1912 and 1955.[87]
Einstein bequeathed the royalties from use of his image to The Hebrew University of Jerusalem. Corbis, successor to The Roger Richman Agency, licenses the use of his name and associated imagery, as agent for the university.[88][89]
In popular culture
Main article: Albert Einstein in popular culture
In the period before World War II, Einstein was so well-known in America that he would be stopped on the street by people wanting him to explain "that theory". He finally figured out a way to handle the incessant inquiries. He told his inquirers "Pardon me, sorry! Always I am mistaken for Professor Einstein."[90]
Einstein has been the subject of or inspiration for many novels, films, plays, and works of music.[91] He is a favorite model for depictions of mad scientists and absent-minded professors; his expressive face and distinctive hairstyle have been widely copied and exaggerated. Time magazine's Frederic Golden wrote that Einstein was "a cartoonist's dream come true".[92]
Awards and honors
Israeli postage stamp (1956).
U.S. postage stamp (1966).
Soviet postage stamp (1979).See also: List of things named after Albert Einstein
In 1922, Einstein was awarded the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics,[93] "for his services to Theoretical Physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect". This refers to his 1905 paper on the photoelectric effect, "On a Heuristic Viewpoint Concerning the Production and Transformation of Light", which was well supported by the experimental evidence by that time. The presentation speech began by mentioning "his theory of relativity [which had] been the subject of lively debate in philosophical circles [and] also has astrophysical implications which are being rigorously examined at the present time". (Einstein 1923)
It was long reported that, in accord with the divorce settlement,[94] the Nobel Prize money had been deposited in a Swiss bank account for Maric to draw on the interest for herself and their two sons, while she could only use the capital by agreement with Einstein. However, personal correspondence made public in 2006[95] shows that he invested much of it in the United States, and saw much of it wiped out in the Great Depression. However, ultimately he paid Maric more money than he received with the prize.[96]
In 1929, Max Planck presented Einstein with the Max Planck medal of the German Physical Society in Berlin, for extraordinary achievements in theoretical physics.[97]
In 1936, Einstein was awarded the Franklin Institute's Franklin Medal for his extensive work on relativity and the photo-electric effect.[97]
The International Union of Pure and Applied Physics named 2005 the "World Year of Physics" in commemoration of the 100th anniversary of the publication of the annus mirabilis papers.[98]
The Albert Einstein Science Park is located on the hill Telegrafenberg in Potsdam, Germany. The best known building in the park is the Einstein Tower which has a bronze bust of Einstein at the entrance. The Tower is an astrophysical observatory that was built to perform checks of Einstein's theory of General Relativity.[99]
The Albert Einstein Memorial in central Washington, D.C. is a monumental bronze statue depicting Einstein seated with manuscript papers in hand. The statue, commissioned in 1979, is located in a grove of trees at the southwest corner of the grounds of the National Academy of Sciences on Constitution Avenue.
The chemical element 99, einsteinium, was named for him in August 1955, four months after Einstein's death.[100][101] 2001 Einstein is an inner main belt asteroid discovered on 5 March 1973.[102]
In 1999 Time magazine named him the Person of the Century,[92][103] ahead of Mahatma Gandhi and Franklin Roosevelt, among others. In the words of a biographer, "to the scientifically literate and the public at large, Einstein is synonymous with genius".[104] Also in 1999, an opinion poll of 100 leading physicists ranked Einstein the "greatest physicist ever".[105] A Gallup poll recorded him as the fourth most admired person of the 20th century in the U.S.[106]
In 1990, his name was added to the Walhalla temple for "laudable and distinguished Germans",[107] which is located east of Regensburg, in Bavaria, Germany.[108]
The United States Postal Service honored Einstein with a Prominent Americans series (1965–1978) 8¢ postage stamp.
Awards named after Einstein
The Albert Einstein Award (sometimes called the Albert Einstein Medal because it is accompanied with a gold medal) is an award in theoretical physics, established to recognize high achievement in the natural sciences. It was endowed by the Lewis and Rosa Strauss Memorial Fund in honor of Albert Einstein's 70th birthday. It was first awarded in 1951 and included a prize money of $15,000,[109][110] which was later reduced to $5,000.[111][112] The winner is selected by a committee (the first of which consisted of Einstein, Oppenheimer, von Neumann and Weyl[113]) of the Institute for Advanced Study, which administers the award.[110]
The Albert Einstein Medal is an award presented by the Albert Einstein Society in Bern, Switzerland. First given in 1979, the award is presented to people who have "rendered outstanding services" in connection with Einstein.[114]
The Albert Einstein Peace Prize is given yearly by the Chicago, Illinois-based Albert Einstein Peace Prize Foundation. Winners of the prize receive $50,000.[115]
See also
Book: Albert Einstein
Wikipedia Books are collections of articles that can be downloaded or ordered in print.
The Einstein Theory of Relativity (educational film about the theory of relativity)
German inventors and discoverers
Heinrich Burkhardt
Hermann Einstein
Historical Museum of Bern (Einstein museum)
History of gravitational theory
Introduction to special relativity
List of coupled cousins
Relativity priority dispute
Sticky bead argument
Summation convention
Publications
The following publications by Albert Einstein are referenced in this article. A more complete list of his publications may be found at List of scientific publications by Albert Einstein.
Einstein, Albert (1901), "Folgerungen aus den Capillaritätserscheinungen (Conclusions Drawn from the Phenomena of Capillarity)", Annalen der Physik 4: 513, Bibcode 1901AnP...309..513E, doi:10.1002/andp.19013090306
Einstein, Albert (1905a), "Über einen die Erzeugung und Verwandlung des Lichtes betreffenden heuristischen Gesichtspunkt (On a Heuristic Viewpoint Concerning the Production and Transformation of Light)", Annalen der Physik 17: 132–148, Bibcode 1905AnP...322..132E, doi:10.1002/andp.19053220607, http://www.physik.uni-augsburg.de/annalen/history/einstein-papers/1905_17_132-148.pdf This annus mirabilis paper on the photoelectric effect was received by Annalen der Physik 18 March.
Einstein, Albert (1905b), A new determination of molecular dimensions . This PhD thesis was completed 30 April and submitted 20 July.
Einstein, Albert (1905c), "On the Motion – Required by the Molecular Kinetic Theory of Heat – of Small Particles Suspended in a Stationary Liquid", Annalen der Physik 17: 549–560 . This annus mirabilis paper on Brownian motion was received 11 May.
Einstein, Albert (1905d), "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies", Annalen der Physik 17: 891–921 . This annus mirabilis paper on special relativity was received 30 June.
Einstein, Albert (1905e), "Does the Inertia of a Body Depend Upon Its Energy Content?", Annalen der Physik 18: 639–641 . This annus mirabilis paper on mass-energy equivalence was received 27 September.
Einstein, Albert (1915), "Die Feldgleichungen der Gravitation (The Field Equations of Gravitation)", Königlich Preussische Akademie der Wissenschaften: 844–847
Einstein, Albert (1917a), "Kosmologische Betrachtungen zur allgemeinen Relativitätstheorie (Cosmological Considerations in the General Theory of Relativity)", Königlich Preussische Akademie der Wissenschaften
Einstein, Albert (1917b), "Zur Quantentheorie der Strahlung (On the Quantum Mechanics of Radiation)", Physikalische Zeitschrift 18: 121–128
Einstein, Albert (11 July 1923), "Fundamental Ideas and Problems of the Theory of Relativity", Nobel Lectures, Physics 1901–1921, Amsterdam: Elsevier Publishing Company, http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/physics/laureates/1921/einstein-lecture.pdf, retrieved 25 March 2007
Einstein, Albert (1924), "Quantentheorie des einatomigen idealen Gases (Quantum theory of monatomic ideal gases)", Sitzungsberichte der Preussichen Akademie der Wissenschaften Physikalisch-Mathematische Klasse: 261–267 . First of a series of papers on this topic.
Einstein, Albert (1926), "Die Ursache der Mäanderbildung der Flussläufe und des sogenannten Baerschen Gesetzes", Die Naturwissenschaften 14: 223–224, Bibcode 1926NW.....14..223E, doi:10.1007/BF01510300 . On Baer's law and meanders in the courses of rivers.
Einstein, Albert; Podolsky, Boris; Rosen, Nathan (15 May 1935), "Can Quantum-Mechanical Description of Physical Reality Be Considered Complete?", Physical Review 47 (10): 777–780, Bibcode 1935PhRv...47..777E, doi:10.1103/PhysRev.47.777
Einstein, Albert (1940), "On Science and Religion", Nature (Edinburgh: Scottish Academic) 146: 605, Bibcode 1940Natur.146..605E, doi:10.1038/146605a0, ISBN 0707304539
Einstein, Albert et al. (4 December 1948), "To the editors", New York Times (Melville, NY: AIP, American Inst. of Physics), ISBN 0735403597, http://phys4.harvard.edu/~wilson/NYTimes1948.html
Einstein, Albert (May 1949), "Why Socialism?", Monthly Review, http://www.monthlyreview.org/598einst.htm, retrieved 16 January 2006
Einstein, Albert (1950), "On the Generalized Theory of Gravitation", Scientific American CLXXXII (4): 13–17
Einstein, Albert (1954), Ideas and Opinions, New York: Random House, ISBN 0-517-00393-7
Einstein, Albert (1969) (in German), Albert Einstein, Hedwig und Max Born: Briefwechsel 1916–1955, Munich: Nymphenburger Verlagshandlung, ISBN 388682005X
Einstein, Albert (1979), Autobiographical Notes, Paul Arthur Schilpp (Centennial ed.), Chicago: Open Court, ISBN 0-875-48352-6 . The chasing a light beam thought experiment is described on pages 48–51.
Collected Papers: Stachel, John, Martin J. Klein, a. J. Kox, Michel Janssen, R. Schulmann, Diana Komos Buchwald and others (Eds.) (1987–2006), The Collected Papers of Albert Einstein, Vol. 1–10, Princeton University Press Further information about the volumes published so far can be found on the webpages of the Einstein Papers Project and on the Princeton University Press Einstein Page
Notes
^ "Albert's intellectual growth was strongly fostered at home. His mother, a talented pianist, ensured the children's musical education. His father regularly read Schiller and Heine aloud to the family. Uncle Jakob challenged Albert with mathematical problems, which he solved with 'a deep feeling of happiness'. Most remarkable was Max Talmud, a poor Jewish medical student from Poland, 'for whom the Jewish community had obtained free meals with the Einstein family'. Talmud came on Thursday nights for about six years, and 'invested his whole person in examining everything that engaged [Albert's] interest'. Talmud had Albert read and discuss many books with him. These included a series of twenty popular science books that convinced Albert 'a lot in the Bible stories could not be true', and a textbook of plane geometry that launched Albert on avid self-study of mathematics, years ahead of the school curriculum. Talmud even had Albert read Kant; as a result Einstein began preaching to his schoolmates about Kant, with 'forcefulness'."[12]
^ "Einstein's greatest intellectual stimulation came from a poor student who dined with his family once a week. It was an old Jewish custom to take in a needy religious scholar to share the Sabbath meal; the Einsteins modified the tradition by hosting instead a medical student on Thursdays. His name was Max Talmud, and he began his weekly visits when he was 21 and Einstein was 10."[13]
References
^ Hans-Josef, Küpper (2000). "Various things about Albert Einstein". einstein-website.de. http://www.einstein-website.de/z_information/variousthings.html. Retrieved 18 July 2009.
^ Zahar, Élie (2001). Poincaré's Philosophy. From Conventionalism to Phenomenology. Carus Publishing Company. p. 41. ISBN 0-8126-9435-X. http://books.google.com/?id=jJl2JAqvoSAC. , Chapter 2, p. 41.
^ "The Nobel Prize in Physics 1921". Nobel Foundation. Archived from the original on 5 October 2008. http://www.webcitation.org/5bLXMl1V0. Retrieved 6 March 2007.
^ a b "Einstein Biography" Nobelprize.org.
^ a b Paul Arthur Schilpp, editor (1951). Albert Einstein: Philosopher-Scientist, Volume II. New York: Harper and Brothers Publishers (Harper Torchbook edition). pp. 730–746. His non-scientific works include: About Zionism: Speeches and Lectures by Professor Albert Einstein (1930), "Why War?" (1933, co-authored by Sigmund Freud), The World As I See It (1934), Out of My Later Years (1950), and a book on science for the general reader, The Evolution of Physics (1938, co-authored by Leopold Infeld).
^ WordNet for Einstein.
^ a b c d e f "Albert Einstein – Biography". Nobel Foundation. http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/physics/laureates/1921/einstein-bio.html. Retrieved 7 March 2007.
^ John J. Stachel (2002). Einstein from "B" to "Z". Springer. pp. 59–61. ISBN 9780817641436. http://books.google.com/books?id=OAsQ_hFjhrAC&pg=PA59. Retrieved 20 February 2011.
^ Einstein's Alleged Handicaps: The Legend of the Dull-Witted Child Who Grew Up to Be a Genius[1]
^ Schilpp (Ed.), P. A. (1979). Albert Einstein – Autobiographical Notes. Open Court Publishing Company. pp. 8–9.
^ Dudley Herschbach, "Einstein as a Student", Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, USA, page 3, web: HarvardChem-Einstein-PDF: Max Talmud visited on Thursdays for six years.
^ Einstein as a Student. (Herschbach, Dudley). from "Einstein for the 21st Century", Princeton University Press, 2008. Retrieved 18 April 2011.
^ "Einstein & Faith". Time.com. 2007-04-05. http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,1607298-1,00.html. Retrieved 2011-04-18.
^ Mehra, Jagdish (2001). "Albert Einstein's first paper" (PDF). The Golden Age of Physics. World Scientific. ISBN 9810249853. http://www.worldscibooks.com/phy_etextbook/4454/4454_chap1.pdf. Retrieved 4 March 2007.
^ Highfield, Roger; Carter, Paul (1993). The Private Lives of Albert Einstein. London: Faber and Faber. p. 21. ISBN 0-571-17170-2.
^ Highfield & Carter (1993, pp. 21,31,56–57)
^ Albert Einstein Collected Papers, vol. 1, 1987, doc. 67.
^ Troemel-Ploetz, D., "Mileva Einstein-Marić: The Woman Who Did Einstein's Mathematics", Women's Studies Int. Forum, vol. 13, no. 5, pp. 415-432, 1990.
^ Walker, Evan Harris (February 1989) (PDF). Did Einstein Espouse his Spouse's Ideas?. Physics Today. http://philosci40.unibe.ch/lehre/winter99/einstein/Walker_Stachel.pdf. Retrieved 2011-03-31.
^ Pais, A., Einstein Lived Here, Oxford University Press, 1994, pp. 1-29.
^ Holton, G., Einstein, History, and Other Passions, Harvard University Press, 1996, pp. 177-193.
^ Stachel, J., Einstein from B to Z, Birkhäuser, 2002, pp. 26-38; 39-55. http://philoscience.unibe.ch/lehre/winter99/einstein/Stachel1966.pdf
^ Martinez, A. A., “Handling evidence in history: the case of Einstein’s Wife.” School Science Review, 86 (316), March 2005, pp. 49-56. http://www.ase.org.uk/htm/members_area/journals/ssr/ssr_march_05pdf/eins_wife-pg49.pdf
^ This conclusion is from Einstein's correspondence with Marić. Lieserl is first mentioned in a letter from Einstein to Marić (who was staying with her family in or near Novi Sad at the time of Lieserl's birth) dated 4 February 1902 (Collected papers Vol. 1, document 134).
^ Albrecht Fölsing (1998). Albert Einstein: A Biography. Penguin Group. ISBN 0140237194; see section I, II,
^ Highfield & Carter 1993, p. 216
^ Now the Swiss Federal Institute of Intellectual Property, http://www.ipi.ch/E/institut/i1.shtm, retrieved 16 October 2006 . See also their FAQ about Einstein and the Institute, http://www.ipi.ch/E/institut/i1094.shtm
^ Peter Galison, "Einstein's Clocks: The Question of Time" Critical Inquiry 26, no. 2 (Winter 2000): 355–389.
^ Gallison, Question of Time.
^ Galison, Peter (2003), Einstein's Clocks, Poincaré's Maps: Empires of Time, New York: W.W. Norton, ISBN 0393020010
^ (Einstein 1905b)
^ "Universität Zürich: Geschichte". Uzh.ch. 2010-12-02. http://www.uzh.ch/about/portrait/history.html. Retrieved 2011-04-03.
^ Kant, Horst. "Albert Einstein and the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Physics in Berlin". in Renn, Jürgen. "Albert Einstein – Chief Engineer of the Universe: One Hundred Authors for Einstein." Ed. Renn, Jürgen. Wiley-VCH. 2005. pp. 166–169. ISBN = 3527405747
^ Calaprice, Alice; Lipscombe, Trevor (2005), Albert Einstein: a biography, Greenwood Publishing Group, p. xix, ISBN 0-313-33080-8, http://books.google.com/?id=5eWh2O_3OAQC , Timeline, p. xix
^ Heilbron, 2000, p. 84.
^ Andrzej, Stasiak (2003), "Myths in science", EMBO reports 4 (3): 236, doi:10.1038/sj.embor.embor779, http://www.nature.com/embor/journal/v4/n3/full/embor779.html, retrieved 31 March 2007
^ Hoffman and Dukas (1972), pp. 145-148; Fölsing (1997), pp. 499-508.
^ a b c d e Isaacson, Walter. Einstein: His Life and Universe, Simon & Schuster (2007)
^ a b c d e Isaacson, Walter. Einstein: His Life and Universe, Simon & Schuster (2007) pp. 407-410
^ "In Brief". Institute for Advanced Study. http://www.ias.edu/people/einstein/in-brief. Retrieved 4 March 2010.
^ Hoffman, B. (1972), pp. 165-171; Fölsing, A. (1997), pp. 666-677.
^ "In Brief (Albert Einstein)". The Center for History of Physics. American Institute of Physics. 2005. http://www.ias.edu/people/einstein/in-brief. Retrieved 2010-11-02.
^ Evans-Pritchard, Ambrose (29 August 2010). "Obama could kill fossil fuels overnight with a nuclear dash for thorium". The Daily Telegraph (London). http://www.telegraph.co.uk/finance/comment/7970619/Obama-could-kill-fossil-fuels-overnight-with-a-nuclear-dash-for-thorium.html.
^ Gosling, F.G. The Manhattan Project: Making the Atomic Bomb, U.S. Department of Energy, History Division (January, 1999) p. vii
^ Diehl, Sarah J.; Moltz, James Clay. Nuclear Weapons and Nonproliferation: a Reference Handbook, ABC-CLIO (2008) p. 218
^ a b Stern, Fritz. Essay, "Einstein's Germany", E = Einstein: His Life, His Thought, and His Influence on Our Culture, Sterling Publishing (2006) pp. 97-118
^ Einstein: The Life and Times by Ronald Clark. page 752
^ Fred Jerome, Rodger Taylor (2006) Einstein on Race and Racism Rutgers University Press, 2006.
^ Calaprice, Alice (2005) The new quotable Einstein. pp.148-149 Princeton University Press, 2005. See also Odyssey in Climate Modeling, Global Warming, and Advising Five Presidents
^ a b "ISRAEL: Einstein Declines". Time magazine. 1 December 1952. http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,817454,00.html. Retrieved 31 March 2010.
^ "Einstein in Princeton / Scientist, Humanitarian, Cultural Icon". Historical Society of Princeton. http://www.princetonhistory.org/museum_alberteinstein.cfm. Retrieved 31 March 2010.
^ The Case of the Scientist with a Pulsating Mass, 14 June 2002, http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/436253, retrieved 11 June 2007
^ Albert Einstein Archives (April 1955), "Draft of projected Telecast Israel Independence Day, April 1955 (last statement ever written)", Einstein Archives Online, http://www.alberteinstein.info/db/ViewImage.do?DocumentID=20078&Page=1, retrieved 14 March 2007
^ Cohen, J.R.; Graver, L.M. (November 1995), "The ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm of Albert Einstein", Surgery, Gynecology & Obstetrics 170 (5): 455–8, PMID 2183375.
^ O'Connor, J.J.; Robertson, E.F. (1997), "Albert Einstein", The MacTutor History of Mathematics archive, School of Mathematics and Statistics, University of St. Andrews, http://www-history.mcs.st-andrews.ac.uk/Biographies/Einstein.html, retrieved 14 March 2007
^ Dr. Albert Einstein Dies in Sleep at 76. World Mourns Loss of Great Scientist., New York Times, 19 April 1955, "Princeton, New Jersey, 18 April 1955. Dr. Albert Einstein, one of the great thinkers of the ages, died in his sleep here early today."
^ The Long, Strange Journey of Einstein's Brain, National Public Radio, http://www.npr.org/templates/story/story.php?storyId=4602913, retrieved 3 October 2007
^ a b "Einstein archive at the Instituut-Lorentz". Instituut-Lorentz. 2005. Retrieved on 21 November 2005.
^ a b Hans-Josef Kuepper. "List of Scientific Publications of Albert Einstein". Einstein-website.de. http://www.einstein-website.de/z_physics/wisspub-e.html. Retrieved 2011-04-03.
^ (Einstein 1905d)
^ Hawking, S. W. (2001), The Universe in short, Bantam Books, ISBN 0-55-380202-X
^ Schwartz, J.; McGuinness, M. (1979), Einstein for Beginners, Pantheon Books, ISBN 0-39-450588-3
^ (Einstein 1905e)
^ For a discussion of the reception of relativity theory around the world, and the different controversies it encountered, see the articles in Thomas F. Glick, ed., The Comparative Reception of Relativity (Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1987), ISBN 9027724989.
^ Pais, Abraham (1982), Subtle is the Lord. The Science and the Life of Albert Einstein, Oxford University Press, pp. 382–386, ISBN 019853907X
^ Einstein, Albert (1905), "Über einen die Erzeugung und Verwandlung des Lichtes betreffenden heuristischen Gesichtspunkt", Annalen der Physik 17: 132–148, Bibcode 1905AnP...322..132E, doi:10.1002/andp.19053220607, http://www.zbp.univie.ac.at/dokumente/einstein1.pdf, retrieved 27 June 2009
^ (Einstein 1905a).
^ http://www.osti.gov/accomplishments/nuggets/einstein/solidcolda.html Celebrating Einstein "Solid Cold". U.S. DOE. Office of Scientific and Technical Information. 2011.
^ Pais, Abraham (1982), Subtle is the Lord. The Science and the Life of Albert Einstein, Oxford University Press, p. 522, ISBN 019853907X
^ Levenson, Thomas. "Einstein's Big Idea". Public Broadcasting Service. 2005. Retrieved on 25 February 2006.
^ Albert Einstein, Nobel lecture in 1921
^ van Dongen, Jeroen (2010) Einstein's Unification Cambridge University Press, p.23.
^ (Einstein 1917a)
^ (Einstein 1917b)
^ (Einstein 1924)
^ Cornell and Wieman Share 2001 Nobel Prize in Physics, 9 October 2001, http://www.nist.gov/public_affairs/releases/n01-04.htm, retrieved 11 June 2007
^ (Einstein 1950)
^ Miller, Arthur I. (1981). Albert Einstein's special theory of relativity. Emergence (1905) and early interpretation (1905–1911). Reading: Addison–Wesley. pp. 325–331. ISBN 0-201-04679-2.
^ Wright, Karen (30 September 2004). "The Master's Mistakes". Discover Magazine. http://discovermagazine.com/2004/sep/the-masters-mistakes/article_view?b_start:int=1&-C=. Retrieved 15 October 2009.
^ Moore, Walter (1989), Schrödinger: Life and Thought, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-43767-9
^ Goettling, Gary. Einstein's refrigerator Georgia Tech Alumni Magazine. 1998. Retrieved on 21 November 2005. Leó Szilárd, a Hungarian physicist who later worked on the Manhattan Project, is credited with the discovery of the chain reaction
^ In September 2008 it was reported that Malcolm McCulloch of Oxford University was heading a three-year project to develop more robust appliances that could be used in locales lacking electricity, and that his team had completed a prototype Einstein refrigerator. He was quoted as saying that improving the design and changing the types of gases used might allow the design's efficiency to be quadrupled.Alok, Jha (21 September 2008), Einstein fridge design can help global cooling, London: The Guardian, http://www.guardian.co.uk/science/2008/sep/21/scienceofclimatechange.climatechange, retrieved 22 February 2011
^ (Einstein 1969). A reprint of this book was published by Edition Erbrich in 1982, ISBN 388682005X
^ (Einstein 1935)
^ Aspect, Alain; Dalibard, Jean; Roger, Gérard (1982). "Experimental test of Bell's inequalities using time-varying analyzers". Physical Review Letters 49 (25): 1804–1807. Bibcode 1982PhRvL..49.1804A. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.49.1804. The first of many experimental tests relating to EPR.
^ "Obituary". New York Times. 1986-07-12. http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9A0DEFD9153FF931A25754C0A960948260. Retrieved 2011-04-03.
^ "Letters Reveal Einstein Love Life", BBC News (BBC), 11 July 2006, http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/5168002.stm, retrieved 14 March 2007
^ Roger Richman Agency (2007), "Albert Einstein Licensing", http://www.albert-einstein.net/index2.html, retrieved 25 March 2007 [dead link]; Archive copy at the Wayback Machine.
^ Einstein, Corbis Rights Representation, http://einstein.biz/, retrieved 8 August 2008
^ The New Yorker April 1939 pg 69 Disguise
^ [2] Einstein's Dream for orchestra by Cindy McTee
^ a b Golden, Frederic (3 January 2000), "Person of the Century: Albert Einstein", Time, http://www.time.com/time/time100/poc/magazine/albert_einstein5a.html, retrieved 25 February 2006
^ Albert Einstein – Frequently Asked Questions, Nobelprize.org, 18 April 1955, http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/physics/laureates/1921/einstein-faq.html, retrieved 7 January 2009
^ Einstein Collected Papers, Vol. 8, doc. 562
^ BBC (11 July 2006), "Letters Reveal Einstein Love Life", BBC News (BBC), http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/5168002.stm, retrieved 25 November 2008
^ MSNBC Report 10 July 2006 [3]
^ a b Marco Mamone Capria (2005) Physics before and after Einstein p.5. IOS Press, 2005
^ World Year of Physics 2005, http://www.wyp2005.org/overview.html, retrieved 3 October 2007
^ Brunhouse, Jay (2008) Maverick Guide to Berlin Pelican Publishing Company
^ Einsteinium and Fermium, http://pubs.acs.org/cen/80th/einsteiniumfermium.html, retrieved 6 June 2009
^ (PDF) History of the International Atomic Energy Agency – The First Forty Years, International Atomic Energy Agency, p. 30, ISBN 9201023979, http://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/publications/PDF/Pub1032_web.pdf, retrieved 6 June 2009
^ Spratt, Christopher E. (April 1990), "The Hungaria group of minor planets", Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada 84 (2): 123–131, Bibcode 1990JRASC..84..123S
^ Isaacson, Walter (3 January 2000), "Person of the Century: Why We Chose Einstein", Time, http://www.time.com/time/time100/poc/magazine/who_mattered_and_why4a.html, retrieved 16 July 2007
^ Howard, Don, and Stachel, John J. Einstein: The Formative Years, 1879–1909, p. 159, Springer (2000)
^ "Einstein the greatest". BBC News. 29 November 1999. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/541840.stm.
^ Mother Teresa Voted by American People as Most Admired Person of the Century, 31 December 1999, http://www.gallup.com/poll/3367/Mother-Teresa-Voted-American-People-Most-Admired-Person-Century.aspx, retrieved 13 August 2008
^ Walhalla, official guide booklet. p. 3. Translated by Helen Stellner and David Hiley, Bernhard Bosse Verlag Regensburg, 2002
^ (in German) Walhalla Ruhmes- und Ehrenhalle, http://www.walhalla-regensburg.de/deutsch/index.shtml, retrieved 3 October 2007
^ Biography of J. Schwinger from University of St Andrews, MacTutor History of Mathematics Archive (Last accessed 17 December 2006).
^ a b The Month at Caltech, April 1954 issue, p. 20 (Last accessed on 4 September 2007).
^ The Americana Annual 1962: An Encyclopedia of the Events of 1961, Americana Corporation, 1962, ISSN 0196-0180
^ Astronautics and Aeronautics, 1967, Scientific and Technical Information Branch, NASA, 1968, ISSN 0519-2366
^ Sigmund, Dawson, Muhlberger (2006), Kurt Godel: The Album, Wiesbaden: Vieweg, ISBN 3834801739
^ Albert Einstein Society in Bern retrieved 17 July 2010
^ Pugwash Online, http://www.pugwash.org/about/history.htm, retrieved 20 December 2009
Further reading
Fölsing, Albrecht (1997): Albert Einstein: A Biography. New York: Penguin Viking. (Translated and abridged from the German by Ewald Osers.)
Hoffmann, Banesh, with the collaboration of Helen Dukas (1972): Albert Einstein: Creator and Rebel. London: Hart-Davis, MacGibbon Ltd.
Isaacson, Walter (2007): Einstein: His Life and Universe. Simon & Schuster Paperbacks, New York. ISBN 9780743264730
Moring, Gary (2004): The complete idiot's guide to understanding Einstein ( 1st ed. 2000). Indianapolis IN: Alpha books (Macmillan USA). ISBN 0028631803
Pais, Abraham (1982): Subtle is the Lord: The science and the life of Albert Einstein. Oxford University Press. The definitive biography to date.
Pais, Abraham (1994): Einstein Lived Here. Oxford University Press.
Parker, Barry (2000): Einstein's Brainchild. Prometheus Books. A review of Einstein's career and accomplishments, written for the lay public.
Schweber, Sylvan S. (2008): Einstein and Oppenheimer: The Meaning of Genius. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0674028289.
Oppenheimer, J.R. (1971): "On Albert Einstein," p. 8-12 in Science and synthesis: an international colloquium organized by Unesco on the tenth anniversary of the death of Albert Einstein and Teilhard de Chardin, Springer-Verlag, 1971, 208 pp. (Lecture delivered at the UNESCO House in Paris on December 13, 1965.) Also published in The New York Review of Books, March 17, 1966, On Albert Einstein by Robert Oppenheimer
External links
Find more about Albert Einstein on Wikipedia's sister projects:
Definitions from Wiktionary
Images and media from Commons
Learning resources from Wikiversity
News stories from Wikinews
Quotations from Wikiquote
Source texts from Wikisource
Textbooks from Wikibooks
Works by Albert Einstein (public domain in Canada)
The MacTutor History of Mathematics archive, School of Mathematics and Statistics, University of St Andrews, Scotland, April 1997, http://www-history.mcs.st-andrews.ac.uk/Biographies/Einstein.html, retrieved 14 June 2009
Why Socialism? by Albert Einstein, Monthly Review, May 1949
Nobelprize.org Biography:Albert Einstein
The Einstein You Never Knew - slideshow by Life magazine
Albert Einstein--Watch Videos
Science Odyssey People And Discoveries
MIT OpenCourseWare STS.042J / 8.225J : Einstein, Oppenheimer, Feynman: Physics in the 20th Century Free, independent study course that explores the changing roles of physics and physicists during the 20th century.
Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein in 1921
Born 14 March 1879(1879-03-14)
Ulm, Kingdom of Württemberg, German Empire
Died 18 April 1955(1955-04-18) (aged 76)
Princeton, New Jersey, United States
Residence Germany, Italy, Switzerland, United States
Citizenship Württemberg/Germany (until 1896)
Stateless (1896–1901)
Switzerland (from 1901)
Austria (1911–12)
Germany (1914–33)
United States (from 1940)[1]
Alma mater ETH Zurich
University of Zurich
Known for General relativity and special relativity
Photoelectric effect
Mass-energy equivalence
Quantification of the Brownian motion
Einstein field equations
Bose–Einstein statistics
Unified Field Theory
Spouse Mileva Marić (1903–1919)
Elsa Löwenthal, née Einstein, (1919–1936)
Awards Nobel Prize in Physics (1921)
Copley Medal (1925)
Max Planck Medal (1929)
Time Person of the Century
Signature
Albert Einstein ( /ˈælbərt ˈaɪnstaɪn/; German: [ˈalbɐt ˈaɪnʃtaɪn] ( listen); 14 March 1879 – 18 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist who discovered the theory of general relativity, effecting a revolution in physics. For this achievement, Einstein is often regarded as the father of modern physics.[2] He received the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics "for his services to theoretical physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect".[3]
Near the beginning of his career, Einstein thought that Newtonian mechanics was no longer enough to reconcile the laws of classical mechanics with the laws of the electromagnetic field. This led to the development of his special theory of relativity. He realized, however, that the principle of relativity could also be extended to gravitational fields, and with his subsequent theory of gravitation in 1916, he published a paper on the general theory of relativity. He continued to deal with problems of statistical mechanics and quantum theory, which led to his explanations of particle theory and the motion of molecules. He also investigated the thermal properties of light which laid the foundation of the photon theory of light. In 1917, Einstein applied the general theory of relativity to model the structure of the universe as a whole.[4]
He was visiting the United States when Hitler came to power in 1933, and did not go back to Germany, where he had been a professor at the Berlin Academy of Sciences. He settled in the U.S., becoming a citizen in 1940. On the eve of World War II, he helped alert President Franklin D. Roosevelt that Germany might be developing an atomic weapon, and recommended that the U.S. begin similar research. Later, together with Bertrand Russell, Einstein signed the Russell–Einstein Manifesto, which highlighted the danger of nuclear weapons. Einstein taught physics at the Institute for Advanced Study at Princeton, New Jersey, until his death in 1955.
Einstein published more than 300 scientific papers along with over 150 non-scientific works.[4][5] His great intelligence and originality have made the word "Einstein" synonymous with genius.[6]
Contents
1 Biography
1.1 Early life and education
1.2 Marriages and children
1.3 Patent office
1.4 Academic career
1.5 Travels abroad
1.6 Emigration from Germany
1.6.1 World War II and the Manhattan Project
1.6.2 U.S. citizenship
1.7 Death
2 Scientific career
2.1 Annus Mirabilis papers
2.2 Thermodynamic fluctuations and statistical physics
2.3 General principles postulated by Einstein
2.4 Theory of relativity and E = mc2
2.5 Photons
2.6 Quantized atomic vibrations
2.7 Adiabatic principle and action-angle variables
2.8 Wave-particle duality
2.9 Theory of critical opalescence
2.10 Zero-point energy
2.11 General relativity and the Equivalence Principle
2.12 Hole argument and Entwurf theory
2.13 Cosmology
2.14 Modern quantum theory
2.15 Bose–Einstein statistics
2.16 Energy momentum pseudotensor
2.17 Unified field theory
2.18 Wormholes
2.19 Einstein–Cartan theory
2.20 Equations of motion
2.21 Einstein's controversial beliefs in physics
2.22 Collaboration with other scientists
2.22.1 Einstein-de Haas experiment
2.22.2 Schrödinger gas model
2.22.3 Einstein refrigerator
2.23 Bohr versus Einstein
2.24 Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen paradox
3 Political and religious views
4 Non-scientific legacy
5 In popular culture
6 Awards and honors
6.1 Awards named after Einstein
7 See also
8 Publications
9 Notes
10 References
11 Further reading
12 External links
Biography
Early life and education
Einstein at the age of 4
Albert Einstein in 1893 (age 14)Albert Einstein was born in Ulm, in the Kingdom of Württemberg in the German Empire on 14 March 1879.[7] His father was Hermann Einstein, a salesman and engineer. His mother was Pauline Einstein (née Koch). In 1880, the family moved to Munich, where his father and his uncle founded Elektrotechnische Fabrik J. Einstein & Cie, a company that manufactured electrical equipment based on direct current.[7]
The Einsteins were non-observant Jews. Albert attended a Catholic elementary school from the age of five for three years. Later, at the age of eight, Einstein was transferred to the Luitpold Gymnasium where he received advanced primary and secondary school education till he left Germany seven years later.[8] Although it has been thought that Einstein had early speech difficulties, this is disputed by the Albert Einstein Archives, and he excelled at the first school that he attended.[9]
His father once showed him a pocket compass; Einstein realized that there must be something causing the needle to move, despite the apparent "empty space".[10] As he grew, Einstein built models and mechanical devices for fun and began to show a talent for mathematics.[7] In 1889, Max Talmud (later changed to Max Talmey) introduced the ten-year old Einstein to key texts in science, mathematics and philosophy, including Immanuel Kant's Critique of Pure Reason and Euclid's Elements (which Einstein called the "holy little geometry book").[11] Talmud was a poor Jewish medical student from Poland. The Jewish community arranged for Talmud to take meals with the Einsteins each week on Thursdays for six years. During this time Talmud wholeheartedly guided Einstein through many secular educational interests.[fn 1][fn 2]
In 1894, his father's company failed: direct current (DC) lost the War of Currents to alternating current (AC). In search of business, the Einstein family moved to Italy, first to Milan and then, a few months later, to Pavia. When the family moved to Pavia, Einstein stayed in Munich to finish his studies at the Luitpold Gymnasium. His father intended for him to pursue electrical engineering, but Einstein clashed with authorities and resented the school's regimen and teaching method. He later wrote that the spirit of learning and creative thought were lost in strict rote learning. In the spring of 1895, he withdrew to join his family in Pavia, convincing the school to let him go by using a doctor's note.[7] During this time, Einstein wrote his first scientific work, "The Investigation of the State of Aether in Magnetic Fields".[14]
Einstein applied directly to the Eidgenössische Polytechnische Schule (ETH) in Zurich, Switzerland. Lacking the requisite Matura certificate, he took an entrance examination, which he failed, although he got exceptional marks in mathematics and physics.[15] The Einsteins sent Albert to Aarau, in northern Switzerland to finish secondary school.[7] While lodging with the family of Professor Jost Winteler, he fell in love with Winteler's daughter, Marie. (His sister Maja later married the Wintelers' son, Paul.)[16] In Aarau, Einstein studied Maxwell's electromagnetic theory. At age 17, he graduated, and, with his father's approval, renounced his citizenship in the German Kingdom of Württemberg to avoid military service, and in 1896 he enrolled in the four year mathematics and physics teaching diploma program at the Polytechnic in Zurich. Marie Winteler moved to Olsberg, Switzerland for a teaching post.
Einstein's future wife, Mileva Marić, also enrolled at the Polytechnic that same year, the only woman among the six students in the mathematics and physics section of the teaching diploma course. Over the next few years, Einstein and Marić's friendship developed into romance, and they read books together on extra-curricular physics in which Einstein was taking an increasing interest. In 1900 Einstein was awarded the Zurich Polytechnic teaching diploma, but Marić failed the examination with a poor grade in the mathematics component, theory of functions.[17] There have been claims that Marić collaborated with Einstein on his celebrated 1905 papers,[18][19] but historians of physics who have studied the issue find no evidence that she made any substantive contributions.[20][21][22][23]
Marriages and children
It has been suggested that Lieserl Einstein be merged into this article or section. (Discuss)
In early 1902, Einstein and Mileva Marić had a daughter they named Lieserl in their correspondence, who was born in Novi Sad where Marić's parents lived.[24] Her full name is not known, and her fate is uncertain after 1903.[25]
Einstein and Marić married in January 1903. In May 1904, the couple's first son, Hans Albert Einstein, was born in Bern, Switzerland. Their second son, Eduard, was born in Zurich in July 1910. In 1914, Einstein moved to Berlin, while his wife remained in Zurich with their sons. Marić and Einstein divorced on 14 February 1919, having lived apart for five years.
Einstein married Elsa Löwenthal (née Einstein) on 2 June 1919, after having had a relationship with her since 1912. She was his first cousin maternally and his second cousin paternally. In 1933, they emigrated permanently to the United States. In 1935, Elsa Einstein was diagnosed with heart and kidney problems and died in December 1936.[26]
Patent office
Left to right: Conrad Habicht, Maurice Solovine and Einstein, who founded the Olympia Academy
Einstein's home in BernAfter graduating, Einstein spent almost two frustrating years searching for a teaching post, but a former classmate's father helped him secure a job in Bern, at the Federal Office for Intellectual Property, the patent office, as an assistant examiner.[27] He evaluated patent applications for electromagnetic devices. In 1903, Einstein's position at the Swiss Patent Office became permanent, although he was passed over for promotion until he "fully mastered machine technology".[28]
Much of his work at the patent office related to questions about transmission of electric signals and electrical-mechanical synchronization of time, two technical problems that show up conspicuously in the thought experiments that eventually led Einstein to his radical conclusions about the nature of light and the fundamental connection between space and time.[29]
With a few friends he met in Bern, Einstein started a small discussion group, self-mockingly named "The Olympia Academy", which met regularly to discuss science and philosophy. Their readings included the works of Henri Poincaré, Ernst Mach, and David Hume, which influenced his scientific and philosophical outlook.
Academic career
Einstein's official 1921 portrait after receiving the Nobel Prize in Physics.In 1901, Einstein had a paper on the capillary forces of a straw published in the prestigious Annalen der Physik.[30] On 30 April 1905, he completed his thesis, with Alfred Kleiner, Professor of Experimental Physics, serving as pro-forma advisor. Einstein was awarded a PhD by the University of Zurich. His dissertation was entitled "A New Determination of Molecular Dimensions".[31] That same year, which has been called Einstein's annus mirabilis or "miracle year", he published four groundbreaking papers, on the photoelectric effect, Brownian motion, special relativity, and the equivalence of matter and energy, which were to bring him to the notice of the academic world.
By 1908, he was recognized as a leading scientist, and he was appointed lecturer at the University of Bern. The following year, he quit the patent office and the lectureship to take the position of physics docent[32] at the University of Zurich. He became a full professor at Karl-Ferdinand University in Prague in 1911. In 1914, he returned to Germany after being appointed director of the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Physics (1914–1932)[33] and a professor at the Humboldt University of Berlin, although with a special clause in his contract that freed him from most teaching obligations. He became a member of the Prussian Academy of Sciences. In 1916, Einstein was appointed president of the German Physical Society (1916–1918).[34][35]
In 1911, he had calculated that, based on his new theory of general relativity, light from another star would be bent by the Sun's gravity. That prediction was claimed confirmed by observations made by a British expedition led by Sir Arthur Eddington during the solar eclipse of May 29, 1919. International media reports of this made Einstein world famous. On 7 November 1919, the leading British newspaper The Times printed a banner headline that read: "Revolution in Science – New Theory of the Universe – Newtonian Ideas Overthrown".[36] (Much later, questions were raised whether the measurements were accurate enough to support Einstein's theory.)
In 1921, Einstein was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics. Because relativity was still considered somewhat controversial, it was officially bestowed for his explanation of the photoelectric effect. He also received the Copley Medal from the Royal Society in 1925.
Travels abroad
Einstein visited New York City for the first time on 2 April 1921, where he received an official welcome by the Mayor, followed by three weeks of lectures and receptions. He went on to deliver several lectures at Columbia University and Princeton University, and in Washington he accompanied representatives of the National Academy of Science on a visit to the White House. On his return to Europe he was the guest of the British statesman and philosopher Viscount Haldane in London, where he met several renowned scientific, intellectual and political figures, and delivered a lecture at Kings College.[37]
In 1922, he traveled throughout Asia and later to Palestine, as part of a six-month excursion and speaking tour. His travels included Singapore, Ceylon, and Japan, where he gave a series of lectures to thousands of Japanese. His first lecture in Tokyo lasted four hours, after which he met the emperor and empress at the Imperial Palace where thousands came to watch. Einstein later gave his impressions of the Japanese in a letter to his sons:[38]:307 "Of all the people I have met, I like the Japanese most, as they are modest, intelligent, considerate, and have a feel for art."[38]:308
On his return voyage, he also visited Palestine for 12 days in what would become his only visit to that region. "He was greeted with great British pomp, as if he were a head of state rather than a theoretical physicist", writes Isaacson. This included a cannon salute upon his arrival at the residence of the British high commissioner, Sir Herbert Samuel. During one reception given to him, the building was "stormed by throngs who wanted to hear him". In Einstein's talk to the audience, he expressed his happiness over the event:
I consider this the greatest day of my life. Before, I have always found something to regret in the Jewish soul, and that is the forgetfulness of its own people. Today, I have been made happy by the sight of the Jewish people learning to recognize themselves and to make themselves recognized as a force in the world.[39]:308
Emigration from Germany
Cartoon of Einstein, who has shed his "Pacifism" wings, standing next to a pillar labeled "World Peace." He is rolling up his sleeves and holding a sword labeled "Preparedness." (circa 1933)In 1933, Einstein decided to emigrate to the United States due to the rise to power of the Nazis under Germany's new chancellor, Adolf Hitler.[40] While visiting American universities in April, 1933, he learned that the new German government had passed a law barring Jews from holding any official positions, including teaching at universities. A month later, the Nazi book burnings occurred, with Einstein's works being among those burnt, and Nazi propaganda minister Joseph Goebbels proclaimed, "Jewish intellectualism is dead."[39] Einstein also learned that his name was on a list of assassination targets, with a "$5,000 bounty on his head". One German magazine included him in a list of enemies of the German regime with the phrase, "not yet hanged".[39]
Einstein was undertaking his third two-month visiting professorship at the California Institute of Technology when Hitler came to power in Germany. On his return to Europe in March 1933 he resided in Belgium for some months, before temporarily moving to England.[41]
He took up a position at the Institute for Advanced Study at Princeton, New Jersey,[42] an affiliation that lasted until his death in 1955. There, he tried to develop a unified field theory and to refute the accepted interpretation of quantum physics, both unsuccessfully. He and Kurt Gödel, another Institute member, became close friends. They would take long walks together discussing their work. His last assistant was Bruria Kaufman, who later became a renowned physicist.
Other scientists also fled to America. Among them were Nobel laureates and professors of theoretical physics. With so many other Jewish scientists now forced by circumstances to live in America, often working side by side, Einstein wrote to a friend, "For me the most beautiful thing is to be in contact with a few fine Jews—a few millennia of a civilized past do mean something after all." In another letter he writes, "In my whole life I have never felt so Jewish as now."[39]
World War II and the Manhattan Project
In 1939, a group of Hungarian scientists that included Hungarian emigre physicist Leo Szilard attempted to alert Washington of ongoing Nazi atomic bomb research. The group's warnings were discounted.[43]
In the summer of 1939, a few months before the beginning of World War II in Europe, Einstein was persuaded to lend his prestige by writing a letter, with Leo Szilard, to President Franklin D. Roosevelt, in order to alert him of the possibility that Nazi Germany might be developing an atomic bomb. At the same time, the letter recommended that the U.S. government should pay attention to and become directly involved with uranium research, and associated chain reaction research. Einstein and Szilard, along with other refugees such as Edward Teller and Eugene Wigner, "regarded it as their responsibility to alert Americans to the possibility that German scientists might win the race to build an atomic bomb, and to warn that Hitler would be more than willing to resort to such a weapon."[38]:630 [44]
The letter is believed to be "arguably the key stimulus for the U.S. adoption of serious investigations into nuclear weapons on the eve of the U.S. entry into World War II".[45] President Roosevelt could not take the risk of allowing Hitler to possess atomic bombs first. As a result of Einstein's letter and his meetings with Roosevelt, the U.S. entered the "race" to develop the bomb, drawing on its "immense material, financial, and scientific resources" to initiate the Manhattan Project. It became the only country to develop an atomic bomb during World War II.
For Einstein, "war was a disease . . . [and] he called for resistance to war." But in 1933, after Hitler assumed full power in Germany, "he renounced pacifism altogether . . . In fact, he urged the Western powers to prepare themselves against another German onslaught."[46]:110 In 1954, a year before his death, Einstein said to his old friend, Linus Pauling, "I made one great mistake in my life — when I signed the letter to President Roosevelt recommending that atom bombs be made; but there was some justification — the danger that the Germans would make them..."[47]
U.S. citizenship
Accepting U.S. citizenship, 1940
Einstein with David Ben Gurion, 1951Einstein became an American citizen in 1940. Not long after settling into his career at Princeton, he expressed his appreciation of the "meritocracy" in American culture when compared to Europe. According to Isaacson, he recognized the "right of individuals to say and think what they pleased", without social barriers, and as result, the individual was "encouraged" to be more creative, a trait he valued from his own early education. Einstein writes:
What makes the new arrival devoted to this country is the democratic trait among the people. No one humbles himself before another person or class. . . American youth has the good fortune not to have its outlook troubled by outworn traditions.[39]:432
As a member of the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People NAACP at Princeton who campaigned for the civil rights of African Americans, Einstein corresponded with civil rights activist W. E. B. Du Bois, and in 1946 Einstein called racism America's "worst disease".[48] He later stated, "Race prejudice has unfortunately become an American tradition which is uncritically handed down from one generation to the next. The only remedies are enlightenment and education".[49]
After the death of Israel's first president, Chaim Weizmann, in November 1952, Prime Minister David Ben-Gurion offered Einstein the position of President of Israel, a mostly ceremonial post.[50] The offer was presented by Israel's ambassador in Washington, Abba Eban, who explained that the offer "embodies the deepest respect which the Jewish people can repose in any of its sons".[38]:522 However, Einstein declined, and wrote in his response that he was "deeply moved", and "at once saddened and ashamed" that he could not accept it:
All my life I have dealt with objective matters, hence I lack both the natural aptitude and the experience to deal properly with people and to exercise official function. I am the more distressed over these circumstances because my relationship with the Jewish people became my strongest human tie once I achieved complete clarity about our precarious position among the nations of the world.[38]:522 [50][51]
Death
The New York World-Telegram announces Einstein's death on April 18, 1955.On April 17, 1955, Albert Einstein experienced internal bleeding caused by the rupture of an abdominal aortic aneurysm, which had previously been reinforced surgically by Dr. Rudolph Nissen in 1948.[52] He took the draft of a speech he was preparing for a television appearance commemorating the State of Israel's seventh anniversary with him to the hospital, but he did not live long enough to complete it.[53] Einstein refused surgery, saying: "I want to go when I want. It is tasteless to prolong life artificially. I have done my share, it is time to go. I will do it elegantly."[54] He died in Princeton Hospital early the next morning at the age of 76, having continued to work until near the end.
Einstein's remains were cremated and his ashes were scattered at an undisclosed location.[55][56] During the autopsy, the pathologist of Princeton Hospital, Thomas Stoltz Harvey, removed Einstein's brain for preservation, without the permission of his family, in hope that the neuroscience of the future would be able to discover what made Einstein so intelligent.[57] In his lecture at Einstein's memorial, nuclear physicist Robert Oppenheimer summarized his impression of him as a person:[46]
"He was almost wholly without sophistication and wholly without worldliness . . . There was always with him a wonderful purity at once childlike and profoundly stubborn."
Scientific career
Albert Einstein in 1904
The photoelectric effect. Incoming photons on the left strike a metal plate (bottom), and eject electrons, depicted as flying off to the right.Throughout his life, Einstein published hundreds of books and articles.[5][7] In addition to the work he did by himself he also collaborated with other scientists on additional projects including the Bose–Einstein statistics, the Einstein refrigerator and others.[58]
Annus Mirabilis papers
Main articles: Annus Mirabilis papers, Photoelectric effect, Special theory of relativity, and Mass–energy equivalence
The Annus Mirabilis papers are four articles pertaining to the photoelectric effect, Brownian motion, the special theory of relativity, and E = mc2 that Albert Einstein published in the Annalen der Physik scientific journal in 1905. These four works contributed substantially to the foundation of modern physics and changed views on space, time, and matter.
Thermodynamic fluctuations and statistical physics
Main article: statistical physics
Albert Einstein's first paper[59] submitted in 1900 to Annalen der Physik was on capillary attraction. It was published in 1901 titled Folgerungen aus den Capillaritätserscheinungen, which was translated as "Conclusions from the capillarity phenomena". Two papers he published in 1902-1903 (thermodynamics) attempted to interpret phenomena from a statistical atomic point of view. These papers were the foundation for the 1905 paper on Brownian motion. These published calculations (1905) showed that Brownian movement can be construed as firm evidence that molecules exist.
His research in 1903 and 1904 was mainly concerned with the effect of finite atomic size on diffusion phenomena.[59] Einstein's theory of Brownian motion was the first paper in the field of statistical physics.[citation needed] It is the most frequently cited, of the Annus Mirabilis papers.[citation needed]
General principles postulated by Einstein
He articulated the principle of relativity. This was understood by Hermann Minkowski to be a generalization of rotational invariance from space to space-time. Other principles postulated by Einstein and later vindicated are the principle of equivalence and the principle of adiabatic invariance of the quantum number. Another of Einstein's general principles, Mach's principle, is fiercely debated, and whether it holds in our world or not is still not definitively established.[citation needed]
Theory of relativity and E = mc2
Main article: History of special relativity
Einstein's "Zur Elektrodynamik bewegter Körper" ("On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies") was received on June 30, 1905 and published September 26 of that same year. It reconciles Maxwell's equations for electricity and magnetism with the laws of mechanics, by introducing major changes to mechanics close to the speed of light. This later became known as Einstein's special theory of relativity.
Consequences of this include the time-space frame of a moving body slowing down and contracting (in the direction of motion) relative to the frame of the observer. This paper also argued that the idea of a luminiferous aether – one of the leading theoretical entities in physics at the time – was superfluous.[60]
In his paper on mass–energy equivalence, which had previously been considered to be distinct concepts, Einstein deduced from his equations of special relativity what has been called the 20th century's best-known equation: E = mc2.[61][62] This equation suggests that tiny amounts of mass could be converted into huge amounts of energy and presaged the development of nuclear power.[63] Einstein's 1905 work on relativity remained controversial for many years, but was accepted by leading physicists, starting with Max Planck.[64][65]
Photons
Main article: Photon
In a 1905 paper,[66] Einstein postulated that light itself consists of localized particles (quanta). Einstein's light quanta were nearly universally rejected by all physicists, including Max Planck and Niels Bohr. This idea only became universally accepted in 1919, with Robert Millikan's detailed experiments on the photoelectric effect, and with the measurement of Compton scattering.
Einstein concluded that each wave of frequency f is associated with a collection of photons with energy hf each, where h is Planck's constant. He does not say much more, because he is not sure how the particles are related to the wave. But he does suggest that this idea would explain certain experimental results, notably the photoelectric effect.[67]
Quantized atomic vibrations
Main article: Einstein solid
In 1907 Einstein proposed a model of matter where each atom in a lattice structure is an independent harmonic oscillator. In the Einstein model, each atom oscillates independently - a series of equally spaced quantized states for each oscillator. Einstein was aware that getting the frequency of the actual oscillations would be different, but he nevertheless proposed this theory because it was a particularly clear demonstration that quantum mechanics could solve the specific heat problem in classical mechanics. Peter Debye refined this model.[68]
This work was the foundation of condensed matter physics.[citation needed]
Adiabatic principle and action-angle variables
Main article: Old quantum theory
Throughout the 1910s, quantum mechanics expanded in scope to cover many different systems. After Ernest Rutherford discovered the nucleus and proposed that electrons orbit like planets, Niels Bohr was able to show that the same quantum mechanical postulates introduced by Planck and developed by Einstein would explain the discrete motion of electrons in atoms, and the periodic table of the elements.
Einstein contributed to these developments by linking them with the 1898 arguments Wilhelm Wien had made. Wien had shown that the hypothesis of adiabatic invariance of a thermal equilibrium state allows all the blackbody curves at different temperature to be derived from one another by a simple shifting process. Einstein noted in 1911 that the same adiabatic principle shows that the quantity which is quantized in any mechanical motion must be an adiabatic invariant. Arnold Sommerfeld identified this adiabatic invariant as the action variable of classical mechanics. The law that the action variable is quantized was a basic principle of the quantum theory as it was known between 1900 and 1925.[citation needed]
Wave-particle duality
Main article: Wave-particle duality
Although the patent office promoted Einstein to Technical Examiner Second Class in 1906, he had not given up on academia. In 1908, he became a privatdozent at the University of Bern.[69] In "über die Entwicklung unserer Anschauungen über das Wesen und die Konstitution der Strahlung" ("The Development of Our Views on the Composition and Essence of Radiation"), on the quantization of light, and in an earlier 1909 paper, Einstein showed that Max Planck's energy quanta must have well-defined momenta and act in some respects as independent, point-like particles. This paper introduced the photon concept (although the name photon was introduced later by Gilbert N. Lewis in 1926) and inspired the notion of wave-particle duality in quantum mechanics.
Theory of critical opalescence
Main article: Critical opalescence
Einstein returned to the problem of thermodynamic fluctuations, giving a treatment of the density variations in a fluid at its critical point. Ordinarily the density fluctuations are controlled by the second derivative of the free energy with respect to the density. At the critical point, this derivative is zero, leading to large fluctuations. The effect of density fluctuations is that light of all wavelengths is scattered, making the fluid look milky white. Einstein relates this to Raleigh scattering, which is what happens when the fluctuation size is much smaller than the wavelength, and which explains why the sky is blue.[70] Einstein quantitatively derived critical opalescence from a treatment of density fluctuations, and demonstrated how both the effect and Rayleigh scattering originate from the atomistic constitution of matter.
Einstein at the Solvay Conference in 1911Zero-point energy
Main article: Zero-point energy
Einstein's physical intuition led him to note that Planck's oscillator energies had an incorrect zero point. He modified Planck's hypothesis by stating that the lowest energy state of an oscillator is equal to 1⁄2hf, to half the energy spacing between levels. This argument, which was made in 1913 in collaboration with Otto Stern, was based on the thermodynamics of a diatomic molecule which can split apart into two free atoms.
General relativity and the Equivalence Principle
Main article: History of general relativity
See also: Principle of equivalence and Theory of relativity
General relativity (GR) is a theory of gravitation that was developed by Albert Einstein between 1907 and 1915. According to general relativity, the observed gravitational attraction between masses results from the warping of space and time by those masses. General relativity has developed into an essential tool in modern astrophysics. It provides the foundation for the current understanding of black holes, regions of space where gravitational attraction is so strong that not even light can escape.
As Albert Einstein later said, the reason for the development of general relativity was that the preference of inertial motions within special relativity was unsatisfactory, while a theory which from the outset prefers no state of motion (even accelerated ones) should appear more satisfactory.[71] So in 1908 he published an article on acceleration under special relativity. In that article, he argued that free fall is really inertial motion, and that for a freefalling observer the rules of special relativity must apply. This argument is called the Equivalence principle. In the same article, Einstein also predicted the phenomenon of gravitational time dilation. In 1911, Einstein published another article expanding on the 1907 article, in which additional effects such as the deflection of light by massive bodies were predicted.
Hole argument and Entwurf theory
Main article: Hole argument
While developing general relativity, Einstein became confused about the gauge invariance in the theory. He formulated an argument that led him to conclude that a general relativistic field theory is impossible. He gave up looking for fully generally covariant tensor equations, and searched for equations that would be invariant under general linear transformations only.
In June, 1913 the Entwurf ("draft") theory was the result of these investigations. As its name suggests, it was a sketch of a theory, with the equations of motion supplemented by additional gauge fixing conditions. Simultaneously less elegant and more difficult than general relativity, after more than two years of intensive work Einstein abandoned the theory in November, 1915 after realizing that the hole argument was mistaken.[72]
Cosmology
Main article: Cosmology
In 1917, Einstein applied the General theory of relativity to model the structure of the universe as a whole. He wanted the universe to be eternal and unchanging, but this type of universe is not consistent with relativity. To fix this, Einstein modified the general theory by introducing a new notion, the cosmological constant. With a positive cosmological constant, the universe could be an eternal static sphere[73]
Einstein believed a spherical static universe is philosophically preferred, because it would obey Mach's principle. He had shown that general relativity incorporates Mach's principle to a certain extent in frame dragging by gravitomagnetic fields, but he knew that Mach's idea would not work if space goes on forever. In a closed universe, he believed that Mach's principle would hold.
Mach's principle has generated much controversy over the years.
Einstein in his office at the University of Berlin.Modern quantum theory
Main article: Schrödinger equation
In 1917, at the height of his work on relativity, Einstein published an article in Physikalische Zeitschrift that proposed the possibility of stimulated emission, the physical process that makes possible the maser and the laser.[74] This article showed that the statistics of absorption and emission of light would only be consistent with Planck's distribution law if the emission of light into a mode with n photons would be enhanced statistically compared to the emission of light into an empty mode. This paper was enormously influential in the later development of quantum mechanics, because it was the first paper to show that the statistics of atomic transitions had simple laws. Einstein discovered Louis de Broglie's work, and supported his ideas, which were received skeptically at first. In another major paper from this era, Einstein gave a wave equation for de Broglie waves, which Einstein suggested was the Hamilton–Jacobi equation of mechanics. This paper would inspire Schrödinger's work of 1926.
Bose–Einstein statistics
Main article: Bose–Einstein condensation
In 1924, Einstein received a description of a statistical model from Indian physicist Satyendra Nath Bose, based on a counting method that assumed that light could be understood as a gas of indistinguishable particles. Einstein noted that Bose's statistics applied to some atoms as well as to the proposed light particles, and submitted his translation of Bose's paper to the Zeitschrift für Physik. Einstein also published his own articles describing the model and its implications, among them the Bose–Einstein condensate phenomenon that some particulates should appear at very low temperatures.[75] It was not until 1995 that the first such condensate was produced experimentally by Eric Allin Cornell and Carl Wieman using ultra-cooling equipment built at the NIST–JILA laboratory at the University of Colorado at Boulder.[76] Bose–Einstein statistics are now used to describe the behaviors of any assembly of bosons. Einstein's sketches for this project may be seen in the Einstein Archive in the library of the Leiden University.[58]
Energy momentum pseudotensor
Main article: Stress-energy-momentum pseudotensor
General relativity includes a dynamical spacetime, so it is difficult to see how to identify the conserved energy and momentum. Noether's theorem allows these quantities to be determined from a Lagrangian with translation invariance, but general covariance makes translation invariance into something of a gauge symmetry. The energy and momentum derived within general relativity by Noether's presecriptions do not make a real tensor for this reason.
Einstein argued that this is true for fundamental reasons, because the gravitational field could be made to vanish by a choice of coordinates. He maintained that the non-covariant energy momentum pseudotensor was in fact the best description of the energy momentum distribution in a gravitational field. This approach has been echoed by Lev Landau and Evgeny Lifshitz, and others, and has become standard.
The use of non-covariant objects like pseudotensors was heavily criticized in 1917 by Erwin Schrödinger and others.
Unified field theory
Main article: Classical unified field theories
Following his research on general relativity, Einstein entered into a series of attempts to generalize his geometric theory of gravitation to include electromagnetism as another aspect of a single entity. In 1950, he described his "unified field theory" in a Scientific American article entitled "On the Generalized Theory of Gravitation".[77] Although he continued to be lauded for his work, Einstein became increasingly isolated in his research, and his efforts were ultimately unsuccessful. In his pursuit of a unification of the fundamental forces, Einstein ignored some mainstream developments in physics, most notably the strong and weak nuclear forces, which were not well understood until many years after his death. Mainstream physics, in turn, largely ignored Einstein's approaches to unification. Einstein's dream of unifying other laws of physics with gravity motivates modern quests for a theory of everything and in particular string theory, where geometrical fields emerge in a unified quantum-mechanical setting.
Wormholes
Main article: Wormhole
Einstein collaborated with others to produce a model of a wormhole. His motivation was to model elementary particles with charge as a solution of gravitational field equations, in line with the program outlined in the paper "Do Gravitational Fields play an Important Role in the Constitution of the Elementary Particles?". These solutions cut and pasted Schwarzschild black holes to make a bridge between two patches.
If one end of a wormhole was positively charged, the other end would be negatively charged. These properties led Einstein to believe that pairs of particles and antiparticles could be described in this way.
Einstein–Cartan theory
Main article: Einstein–Cartan theory
In order to incorporate spinning point particles into general relativity, the affine connection needed to be generalized to include an antisymmetric part, called the torsion. This modification was made by Einstein and Cartan in the 1920s.
Equations of motion
Main article: Einstein–Infeld–Hoffmann equations
The theory of general relativity has a fundamental law – the Einstein equations which describe how space curves, the geodesic equation which describes how particles move may be derived from the Einstein equations.
Since the equations of general relativity are non-linear, a lump of energy made out of pure gravitational fields, like a black hole, would move on a trajectory which is determined by the Einstein equations themselves, not by a new law. So Einstein proposed that the path of a singular solution, like a black hole, would be determined to be a geodesic from general relativity itself.
This was established by Einstein, Infeld, and Hoffmann for pointlike objects without angular momentum, and by Roy Kerr for spinning objects.
Einstein's controversial beliefs in physics
In addition to his well-accepted results, some of Einstein's views are regarded as controversial:
In the special relativity paper (in 1905), Einstein noted that, given a specific definition of the word "force" (a definition which he later agreed was not advantageous), and if we choose to maintain (by convention) the equation mass x acceleration = force, then one arrives at as the expression for the transverse mass of a fast moving particle. This differs from the accepted expression today, because, as noted in the footnotes to Einstein's paper added in the 1913 reprint, "it is more to the point to define force in such a way that the laws of energy and momentum assume the simplest form", as was done, for example, by Max Planck in 1906, who gave the now familiar expression for the transverse mass. As Miller points out, this is equivalent to the transverse mass predictions of both Einstein and Lorentz. Einstein had commented already in the 1905 paper that "With a different definition of force and acceleration, we should naturally obtain other expressions for the masses. This shows that in comparing different theories... we must proceed very cautiously."[78]
Einstein published (in 1922) a qualitative theory of superconductivity based on the vague idea of electrons shared in orbits. This paper predated modern quantum mechanics, and today is regarded as being incorrect. The current theory of low temperature superconductivity was only worked out in 1957, thirty years after the establishing of modern quantum mechanics. However, even today, superconductivity is not well understood, and alternative theories continue to be put forward, especially to account for high-temperature superconductors.[citation needed]
After introducing the concept of gravitational waves in 1917, Einstein subsequently entertained doubts about whether they could be physically realized. In 1937 he published a paper saying that the focusing properties of geodesics in general relativity would lead to an instability which causes plane gravitational waves to collapse in on themselves. While this is true to a certain extent in some limits, because gravitational instabilities can lead to a concentration of energy density into black holes, for plane waves of the type Einstein and Rosen considered in their paper, the instabilities are under control. Einstein retracted this position a short time later.[citation needed]
Einstein denied several times that black holes could form. In 1939 he published a paper that argues that a star collapsing would spin faster and faster, spinning at the speed of light with infinite energy well before the point where it is about to collapse into a black hole. This paper received no citations, and the conclusions are well understood to be wrong. Einstein's argument itself is inconclusive, since he only shows that stable spinning objects have to spin faster and faster to stay stable before the point where they collapse. But it is well understood today (and was understood well by some even then) that collapse cannot happen through stationary states the way Einstein imagined. Nevertheless, the extent to which the models of black holes in classical general relativity correspond to physical reality remains unclear, and in particular the implications of the central singularity implicit in these models are still not understood. Efforts to conclusively prove the existence of event horizons have still not been successful.[citation needed]
Closely related to his rejection of black holes, Einstein believed that the exclusion of singularities might restrict the class of solutions of the field equations so as to force solutions compatible with quantum mechanics, but no such theory has ever been found.[citation needed]
In the early days of quantum mechanics, Einstein tried to show that the uncertainty principle was not valid, but by 1927 he had become convinced that it was valid.[citation needed]
In the EPR paper, Einstein argued that quantum mechanics cannot be a complete realistic and local representation of phenomena, given specific definitions of "realism", "locality", and "completeness". The modern consensus is that Einstein's concept of realism is too restrictive.[citation needed]
Einstein himself considered the introduction of the cosmological term in his 1917 paper founding cosmology as a "blunder".[79] The theory of general relativity predicted an expanding or contracting universe, but Einstein wanted a universe which is an unchanging three dimensional sphere, like the surface of a three dimensional ball in four dimensions. He wanted this for philosophical reasons, so as to incorporate Mach's principle in a reasonable way. He stabilized his solution by introducing a cosmological constant, and when the universe was shown to be expanding, he retracted the constant as a blunder. This is not really much of a blunder – the cosmological constant is necessary within general relativity as it is currently understood, and it is widely believed to have a nonzero value today.
Einstein did not immediately appreciate the value of Minkowski's four-dimensional formulation of special relativity, although within a few years he had adopted it as the basis for his theory of gravitation.[citation needed]
Finding it too formal, Einstein believed that Heisenberg's matrix mechanics was incorrect. He changed his mind when Schrödinger and others demonstrated that the formulation in terms of the Schrödinger equation, based on Einstein's wave-particle duality was equivalent to Heisenberg's matrices.[citation needed]
Collaboration with other scientists
In addition to long time collaborators Leopold Infeld, Nathan Rosen, Peter Bergmann and others, Einstein also had some one-shot collaborations with various scientists.
Einstein-de Haas experiment
Main article: Einstein-de Haas effect
Einstein and De Haas demonstrated that magnetization is due to the motion of electrons, nowadays known to be the spin. In order to show this, they reversed the magnetization in an iron bar suspended on a torsion pendulum. They confirmed that this leads the bar to rotate, because the electron's angular momentum changes as the magnetization changes. This experiment needed to be sensitive, because the angular momentum associated with electrons is small, but it definitively established that electron motion of some kind is responsible for magnetization.
Schrödinger gas model
Einstein suggested to Erwin Schrödinger that he might be able to reproduce the statistics of a Bose–Einstein gas by considering a box. Then to each possible quantum motion of a particle in a box associate an independent harmonic oscillator. Quantizing these oscillators, each level will have an integer occupation number, which will be the number of particles in it.
This formulation is a form of second quantization, but it predates modern quantum mechanics. Erwin Schrödinger applied this to derive the thermodynamic properties of a semiclassical[disambiguation needed] ideal gas. Schrödinger urged Einstein to add his name as co-author, although Einstein declined the invitation.[80]
Einstein refrigerator
Main article: Einstein refrigerator
In 1926, Einstein and his former student Leó Szilárd co-invented (and in 1930, patented) the Einstein refrigerator. This absorption refrigerator was then revolutionary for having no moving parts and using only heat as an input.[81] On 11 November 1930, U.S. Patent 1,781,541 was awarded to Albert Einstein and Leó Szilárd for the refrigerator. Their invention was not immediately put into commercial production, as the most promising of their patents were quickly bought up by the Swedish company Electrolux to protect its refrigeration technology from competition.[82]
Bohr versus Einstein
Main article: Bohr–Einstein debates
Einstein and Niels Bohr, 1925In the 1920s, quantum mechanics developed into a more complete theory. Einstein was unhappy with the Copenhagen interpretation of quantum theory developed by Niels Bohr and Werner Heisenberg, both in its outcomes and its instrumentalist methodology, Einstein being a scientific realist. In this interpretation, quantum phenomena are inherently probabilistic, with definite states resulting only upon interaction with classical systems. A public debate between Einstein and Bohr followed, lasting on and off for many years (including during the Solvay Conferences). Einstein formulated thought experiments against the Copenhagen interpretation, which were all rebutted by Bohr. In a 1926 letter to Max Born, Einstein wrote: "I, at any rate, am convinced that He [God] does not throw dice."[83]
Einstein was never satisfied by what he perceived to be quantum theory's intrinsically incomplete description of nature, and in 1935 he further explored the issue in collaboration with Boris Podolsky and Nathan Rosen, noting that the theory seems to require non-local interactions; this is known as the EPR paradox.[84] The EPR experiment has since been performed, with results confirming quantum theory's predictions.[85] Repercussions of the Einstein–Bohr debate have found their way into philosophical discourse.
Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen paradox
Main article: EPR paradox
In 1935, Einstein returned to the question of quantum mechanics. He considered how a measurement on one of two entangled particles would affect the other. He noted, along with his collaborators, that by performing different measurements on the distant particle, either of position or momentum, different properties of the entangled partner could be discovered without disturbing it in any way.
He then used a hypothesis of local realism to conclude that the other particle had these properties already determined. The principle he proposed is that if it is possible to determine what the answer to a position or momentum measurement would be, without in any way disturbing the particle, then the particle actually has values of position or momentum.
This principle distilled the essence of Einstein's objection to quantum mechanics. As a physical principle, it has since been shown to be incompatible with experiments.
Political and religious views
Main articles: Albert Einstein's political views and Albert Einstein's religious views
Albert Einstein, seen here with his wife Elsa Einstein and Zionist leaders, including future President of Israel Chaim Weizmann, his wife Dr. Vera Weizmann, Menahem Ussishkin, and Ben-Zion Mossinson on arrival in New York City in 1921.Albert Einstein's political views emerged publicly in the middle of the 20th century due to his fame and reputation for genius. Einstein offered to and was called on to give judgments and opinions on matters often unrelated to theoretical physics or mathematics. (see main article)
Einstein's views on religious belief have been collected from interviews and original writings. These views covered theological determinism, agnosticism, humanism along with ethical culture, opting for Spinoza's god over belief in a personal god, religious belief, enlightenment and liberation, Jews, Christianity, Jesus, Pope Pius XII, and the Catholic Church. (see main article)
Non-scientific legacy
While travelling, Einstein wrote daily to his wife Elsa and adopted stepdaughters Margot and Ilse. The letters were included in the papers bequeathed to The Hebrew University. Margot Einstein permitted the personal letters to be made available to the public, but requested that it not be done until twenty years after her death (she died in 1986[86]). Barbara Wolff, of The Hebrew University's Albert Einstein Archives, told the BBC that there are about 3,500 pages of private correspondence written between 1912 and 1955.[87]
Einstein bequeathed the royalties from use of his image to The Hebrew University of Jerusalem. Corbis, successor to The Roger Richman Agency, licenses the use of his name and associated imagery, as agent for the university.[88][89]
In popular culture
Main article: Albert Einstein in popular culture
In the period before World War II, Einstein was so well-known in America that he would be stopped on the street by people wanting him to explain "that theory". He finally figured out a way to handle the incessant inquiries. He told his inquirers "Pardon me, sorry! Always I am mistaken for Professor Einstein."[90]
Einstein has been the subject of or inspiration for many novels, films, plays, and works of music.[91] He is a favorite model for depictions of mad scientists and absent-minded professors; his expressive face and distinctive hairstyle have been widely copied and exaggerated. Time magazine's Frederic Golden wrote that Einstein was "a cartoonist's dream come true".[92]
Awards and honors
Israeli postage stamp (1956).
U.S. postage stamp (1966).
Soviet postage stamp (1979).See also: List of things named after Albert Einstein
In 1922, Einstein was awarded the 1921 Nobel Prize in Physics,[93] "for his services to Theoretical Physics, and especially for his discovery of the law of the photoelectric effect". This refers to his 1905 paper on the photoelectric effect, "On a Heuristic Viewpoint Concerning the Production and Transformation of Light", which was well supported by the experimental evidence by that time. The presentation speech began by mentioning "his theory of relativity [which had] been the subject of lively debate in philosophical circles [and] also has astrophysical implications which are being rigorously examined at the present time". (Einstein 1923)
It was long reported that, in accord with the divorce settlement,[94] the Nobel Prize money had been deposited in a Swiss bank account for Maric to draw on the interest for herself and their two sons, while she could only use the capital by agreement with Einstein. However, personal correspondence made public in 2006[95] shows that he invested much of it in the United States, and saw much of it wiped out in the Great Depression. However, ultimately he paid Maric more money than he received with the prize.[96]
In 1929, Max Planck presented Einstein with the Max Planck medal of the German Physical Society in Berlin, for extraordinary achievements in theoretical physics.[97]
In 1936, Einstein was awarded the Franklin Institute's Franklin Medal for his extensive work on relativity and the photo-electric effect.[97]
The International Union of Pure and Applied Physics named 2005 the "World Year of Physics" in commemoration of the 100th anniversary of the publication of the annus mirabilis papers.[98]
The Albert Einstein Science Park is located on the hill Telegrafenberg in Potsdam, Germany. The best known building in the park is the Einstein Tower which has a bronze bust of Einstein at the entrance. The Tower is an astrophysical observatory that was built to perform checks of Einstein's theory of General Relativity.[99]
The Albert Einstein Memorial in central Washington, D.C. is a monumental bronze statue depicting Einstein seated with manuscript papers in hand. The statue, commissioned in 1979, is located in a grove of trees at the southwest corner of the grounds of the National Academy of Sciences on Constitution Avenue.
The chemical element 99, einsteinium, was named for him in August 1955, four months after Einstein's death.[100][101] 2001 Einstein is an inner main belt asteroid discovered on 5 March 1973.[102]
In 1999 Time magazine named him the Person of the Century,[92][103] ahead of Mahatma Gandhi and Franklin Roosevelt, among others. In the words of a biographer, "to the scientifically literate and the public at large, Einstein is synonymous with genius".[104] Also in 1999, an opinion poll of 100 leading physicists ranked Einstein the "greatest physicist ever".[105] A Gallup poll recorded him as the fourth most admired person of the 20th century in the U.S.[106]
In 1990, his name was added to the Walhalla temple for "laudable and distinguished Germans",[107] which is located east of Regensburg, in Bavaria, Germany.[108]
The United States Postal Service honored Einstein with a Prominent Americans series (1965–1978) 8¢ postage stamp.
Awards named after Einstein
The Albert Einstein Award (sometimes called the Albert Einstein Medal because it is accompanied with a gold medal) is an award in theoretical physics, established to recognize high achievement in the natural sciences. It was endowed by the Lewis and Rosa Strauss Memorial Fund in honor of Albert Einstein's 70th birthday. It was first awarded in 1951 and included a prize money of $15,000,[109][110] which was later reduced to $5,000.[111][112] The winner is selected by a committee (the first of which consisted of Einstein, Oppenheimer, von Neumann and Weyl[113]) of the Institute for Advanced Study, which administers the award.[110]
The Albert Einstein Medal is an award presented by the Albert Einstein Society in Bern, Switzerland. First given in 1979, the award is presented to people who have "rendered outstanding services" in connection with Einstein.[114]
The Albert Einstein Peace Prize is given yearly by the Chicago, Illinois-based Albert Einstein Peace Prize Foundation. Winners of the prize receive $50,000.[115]
See also
Book: Albert Einstein
Wikipedia Books are collections of articles that can be downloaded or ordered in print.
The Einstein Theory of Relativity (educational film about the theory of relativity)
German inventors and discoverers
Heinrich Burkhardt
Hermann Einstein
Historical Museum of Bern (Einstein museum)
History of gravitational theory
Introduction to special relativity
List of coupled cousins
Relativity priority dispute
Sticky bead argument
Summation convention
Publications
The following publications by Albert Einstein are referenced in this article. A more complete list of his publications may be found at List of scientific publications by Albert Einstein.
Einstein, Albert (1901), "Folgerungen aus den Capillaritätserscheinungen (Conclusions Drawn from the Phenomena of Capillarity)", Annalen der Physik 4: 513, Bibcode 1901AnP...309..513E, doi:10.1002/andp.19013090306
Einstein, Albert (1905a), "Über einen die Erzeugung und Verwandlung des Lichtes betreffenden heuristischen Gesichtspunkt (On a Heuristic Viewpoint Concerning the Production and Transformation of Light)", Annalen der Physik 17: 132–148, Bibcode 1905AnP...322..132E, doi:10.1002/andp.19053220607, http://www.physik.uni-augsburg.de/annalen/history/einstein-papers/1905_17_132-148.pdf This annus mirabilis paper on the photoelectric effect was received by Annalen der Physik 18 March.
Einstein, Albert (1905b), A new determination of molecular dimensions . This PhD thesis was completed 30 April and submitted 20 July.
Einstein, Albert (1905c), "On the Motion – Required by the Molecular Kinetic Theory of Heat – of Small Particles Suspended in a Stationary Liquid", Annalen der Physik 17: 549–560 . This annus mirabilis paper on Brownian motion was received 11 May.
Einstein, Albert (1905d), "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies", Annalen der Physik 17: 891–921 . This annus mirabilis paper on special relativity was received 30 June.
Einstein, Albert (1905e), "Does the Inertia of a Body Depend Upon Its Energy Content?", Annalen der Physik 18: 639–641 . This annus mirabilis paper on mass-energy equivalence was received 27 September.
Einstein, Albert (1915), "Die Feldgleichungen der Gravitation (The Field Equations of Gravitation)", Königlich Preussische Akademie der Wissenschaften: 844–847
Einstein, Albert (1917a), "Kosmologische Betrachtungen zur allgemeinen Relativitätstheorie (Cosmological Considerations in the General Theory of Relativity)", Königlich Preussische Akademie der Wissenschaften
Einstein, Albert (1917b), "Zur Quantentheorie der Strahlung (On the Quantum Mechanics of Radiation)", Physikalische Zeitschrift 18: 121–128
Einstein, Albert (11 July 1923), "Fundamental Ideas and Problems of the Theory of Relativity", Nobel Lectures, Physics 1901–1921, Amsterdam: Elsevier Publishing Company, http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/physics/laureates/1921/einstein-lecture.pdf, retrieved 25 March 2007
Einstein, Albert (1924), "Quantentheorie des einatomigen idealen Gases (Quantum theory of monatomic ideal gases)", Sitzungsberichte der Preussichen Akademie der Wissenschaften Physikalisch-Mathematische Klasse: 261–267 . First of a series of papers on this topic.
Einstein, Albert (1926), "Die Ursache der Mäanderbildung der Flussläufe und des sogenannten Baerschen Gesetzes", Die Naturwissenschaften 14: 223–224, Bibcode 1926NW.....14..223E, doi:10.1007/BF01510300 . On Baer's law and meanders in the courses of rivers.
Einstein, Albert; Podolsky, Boris; Rosen, Nathan (15 May 1935), "Can Quantum-Mechanical Description of Physical Reality Be Considered Complete?", Physical Review 47 (10): 777–780, Bibcode 1935PhRv...47..777E, doi:10.1103/PhysRev.47.777
Einstein, Albert (1940), "On Science and Religion", Nature (Edinburgh: Scottish Academic) 146: 605, Bibcode 1940Natur.146..605E, doi:10.1038/146605a0, ISBN 0707304539
Einstein, Albert et al. (4 December 1948), "To the editors", New York Times (Melville, NY: AIP, American Inst. of Physics), ISBN 0735403597, http://phys4.harvard.edu/~wilson/NYTimes1948.html
Einstein, Albert (May 1949), "Why Socialism?", Monthly Review, http://www.monthlyreview.org/598einst.htm, retrieved 16 January 2006
Einstein, Albert (1950), "On the Generalized Theory of Gravitation", Scientific American CLXXXII (4): 13–17
Einstein, Albert (1954), Ideas and Opinions, New York: Random House, ISBN 0-517-00393-7
Einstein, Albert (1969) (in German), Albert Einstein, Hedwig und Max Born: Briefwechsel 1916–1955, Munich: Nymphenburger Verlagshandlung, ISBN 388682005X
Einstein, Albert (1979), Autobiographical Notes, Paul Arthur Schilpp (Centennial ed.), Chicago: Open Court, ISBN 0-875-48352-6 . The chasing a light beam thought experiment is described on pages 48–51.
Collected Papers: Stachel, John, Martin J. Klein, a. J. Kox, Michel Janssen, R. Schulmann, Diana Komos Buchwald and others (Eds.) (1987–2006), The Collected Papers of Albert Einstein, Vol. 1–10, Princeton University Press Further information about the volumes published so far can be found on the webpages of the Einstein Papers Project and on the Princeton University Press Einstein Page
Notes
^ "Albert's intellectual growth was strongly fostered at home. His mother, a talented pianist, ensured the children's musical education. His father regularly read Schiller and Heine aloud to the family. Uncle Jakob challenged Albert with mathematical problems, which he solved with 'a deep feeling of happiness'. Most remarkable was Max Talmud, a poor Jewish medical student from Poland, 'for whom the Jewish community had obtained free meals with the Einstein family'. Talmud came on Thursday nights for about six years, and 'invested his whole person in examining everything that engaged [Albert's] interest'. Talmud had Albert read and discuss many books with him. These included a series of twenty popular science books that convinced Albert 'a lot in the Bible stories could not be true', and a textbook of plane geometry that launched Albert on avid self-study of mathematics, years ahead of the school curriculum. Talmud even had Albert read Kant; as a result Einstein began preaching to his schoolmates about Kant, with 'forcefulness'."[12]
^ "Einstein's greatest intellectual stimulation came from a poor student who dined with his family once a week. It was an old Jewish custom to take in a needy religious scholar to share the Sabbath meal; the Einsteins modified the tradition by hosting instead a medical student on Thursdays. His name was Max Talmud, and he began his weekly visits when he was 21 and Einstein was 10."[13]
References
^ Hans-Josef, Küpper (2000). "Various things about Albert Einstein". einstein-website.de. http://www.einstein-website.de/z_information/variousthings.html. Retrieved 18 July 2009.
^ Zahar, Élie (2001). Poincaré's Philosophy. From Conventionalism to Phenomenology. Carus Publishing Company. p. 41. ISBN 0-8126-9435-X. http://books.google.com/?id=jJl2JAqvoSAC. , Chapter 2, p. 41.
^ "The Nobel Prize in Physics 1921". Nobel Foundation. Archived from the original on 5 October 2008. http://www.webcitation.org/5bLXMl1V0. Retrieved 6 March 2007.
^ a b "Einstein Biography" Nobelprize.org.
^ a b Paul Arthur Schilpp, editor (1951). Albert Einstein: Philosopher-Scientist, Volume II. New York: Harper and Brothers Publishers (Harper Torchbook edition). pp. 730–746. His non-scientific works include: About Zionism: Speeches and Lectures by Professor Albert Einstein (1930), "Why War?" (1933, co-authored by Sigmund Freud), The World As I See It (1934), Out of My Later Years (1950), and a book on science for the general reader, The Evolution of Physics (1938, co-authored by Leopold Infeld).
^ WordNet for Einstein.
^ a b c d e f "Albert Einstein – Biography". Nobel Foundation. http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/physics/laureates/1921/einstein-bio.html. Retrieved 7 March 2007.
^ John J. Stachel (2002). Einstein from "B" to "Z". Springer. pp. 59–61. ISBN 9780817641436. http://books.google.com/books?id=OAsQ_hFjhrAC&pg=PA59. Retrieved 20 February 2011.
^ Einstein's Alleged Handicaps: The Legend of the Dull-Witted Child Who Grew Up to Be a Genius[1]
^ Schilpp (Ed.), P. A. (1979). Albert Einstein – Autobiographical Notes. Open Court Publishing Company. pp. 8–9.
^ Dudley Herschbach, "Einstein as a Student", Department of Chemistry and Chemical Biology, Harvard University, Cambridge, MA, USA, page 3, web: HarvardChem-Einstein-PDF: Max Talmud visited on Thursdays for six years.
^ Einstein as a Student. (Herschbach, Dudley). from "Einstein for the 21st Century", Princeton University Press, 2008. Retrieved 18 April 2011.
^ "Einstein & Faith". Time.com. 2007-04-05. http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,1607298-1,00.html. Retrieved 2011-04-18.
^ Mehra, Jagdish (2001). "Albert Einstein's first paper" (PDF). The Golden Age of Physics. World Scientific. ISBN 9810249853. http://www.worldscibooks.com/phy_etextbook/4454/4454_chap1.pdf. Retrieved 4 March 2007.
^ Highfield, Roger; Carter, Paul (1993). The Private Lives of Albert Einstein. London: Faber and Faber. p. 21. ISBN 0-571-17170-2.
^ Highfield & Carter (1993, pp. 21,31,56–57)
^ Albert Einstein Collected Papers, vol. 1, 1987, doc. 67.
^ Troemel-Ploetz, D., "Mileva Einstein-Marić: The Woman Who Did Einstein's Mathematics", Women's Studies Int. Forum, vol. 13, no. 5, pp. 415-432, 1990.
^ Walker, Evan Harris (February 1989) (PDF). Did Einstein Espouse his Spouse's Ideas?. Physics Today. http://philosci40.unibe.ch/lehre/winter99/einstein/Walker_Stachel.pdf. Retrieved 2011-03-31.
^ Pais, A., Einstein Lived Here, Oxford University Press, 1994, pp. 1-29.
^ Holton, G., Einstein, History, and Other Passions, Harvard University Press, 1996, pp. 177-193.
^ Stachel, J., Einstein from B to Z, Birkhäuser, 2002, pp. 26-38; 39-55. http://philoscience.unibe.ch/lehre/winter99/einstein/Stachel1966.pdf
^ Martinez, A. A., “Handling evidence in history: the case of Einstein’s Wife.” School Science Review, 86 (316), March 2005, pp. 49-56. http://www.ase.org.uk/htm/members_area/journals/ssr/ssr_march_05pdf/eins_wife-pg49.pdf
^ This conclusion is from Einstein's correspondence with Marić. Lieserl is first mentioned in a letter from Einstein to Marić (who was staying with her family in or near Novi Sad at the time of Lieserl's birth) dated 4 February 1902 (Collected papers Vol. 1, document 134).
^ Albrecht Fölsing (1998). Albert Einstein: A Biography. Penguin Group. ISBN 0140237194; see section I, II,
^ Highfield & Carter 1993, p. 216
^ Now the Swiss Federal Institute of Intellectual Property, http://www.ipi.ch/E/institut/i1.shtm, retrieved 16 October 2006 . See also their FAQ about Einstein and the Institute, http://www.ipi.ch/E/institut/i1094.shtm
^ Peter Galison, "Einstein's Clocks: The Question of Time" Critical Inquiry 26, no. 2 (Winter 2000): 355–389.
^ Gallison, Question of Time.
^ Galison, Peter (2003), Einstein's Clocks, Poincaré's Maps: Empires of Time, New York: W.W. Norton, ISBN 0393020010
^ (Einstein 1905b)
^ "Universität Zürich: Geschichte". Uzh.ch. 2010-12-02. http://www.uzh.ch/about/portrait/history.html. Retrieved 2011-04-03.
^ Kant, Horst. "Albert Einstein and the Kaiser Wilhelm Institute for Physics in Berlin". in Renn, Jürgen. "Albert Einstein – Chief Engineer of the Universe: One Hundred Authors for Einstein." Ed. Renn, Jürgen. Wiley-VCH. 2005. pp. 166–169. ISBN = 3527405747
^ Calaprice, Alice; Lipscombe, Trevor (2005), Albert Einstein: a biography, Greenwood Publishing Group, p. xix, ISBN 0-313-33080-8, http://books.google.com/?id=5eWh2O_3OAQC , Timeline, p. xix
^ Heilbron, 2000, p. 84.
^ Andrzej, Stasiak (2003), "Myths in science", EMBO reports 4 (3): 236, doi:10.1038/sj.embor.embor779, http://www.nature.com/embor/journal/v4/n3/full/embor779.html, retrieved 31 March 2007
^ Hoffman and Dukas (1972), pp. 145-148; Fölsing (1997), pp. 499-508.
^ a b c d e Isaacson, Walter. Einstein: His Life and Universe, Simon & Schuster (2007)
^ a b c d e Isaacson, Walter. Einstein: His Life and Universe, Simon & Schuster (2007) pp. 407-410
^ "In Brief". Institute for Advanced Study. http://www.ias.edu/people/einstein/in-brief. Retrieved 4 March 2010.
^ Hoffman, B. (1972), pp. 165-171; Fölsing, A. (1997), pp. 666-677.
^ "In Brief (Albert Einstein)". The Center for History of Physics. American Institute of Physics. 2005. http://www.ias.edu/people/einstein/in-brief. Retrieved 2010-11-02.
^ Evans-Pritchard, Ambrose (29 August 2010). "Obama could kill fossil fuels overnight with a nuclear dash for thorium". The Daily Telegraph (London). http://www.telegraph.co.uk/finance/comment/7970619/Obama-could-kill-fossil-fuels-overnight-with-a-nuclear-dash-for-thorium.html.
^ Gosling, F.G. The Manhattan Project: Making the Atomic Bomb, U.S. Department of Energy, History Division (January, 1999) p. vii
^ Diehl, Sarah J.; Moltz, James Clay. Nuclear Weapons and Nonproliferation: a Reference Handbook, ABC-CLIO (2008) p. 218
^ a b Stern, Fritz. Essay, "Einstein's Germany", E = Einstein: His Life, His Thought, and His Influence on Our Culture, Sterling Publishing (2006) pp. 97-118
^ Einstein: The Life and Times by Ronald Clark. page 752
^ Fred Jerome, Rodger Taylor (2006) Einstein on Race and Racism Rutgers University Press, 2006.
^ Calaprice, Alice (2005) The new quotable Einstein. pp.148-149 Princeton University Press, 2005. See also Odyssey in Climate Modeling, Global Warming, and Advising Five Presidents
^ a b "ISRAEL: Einstein Declines". Time magazine. 1 December 1952. http://www.time.com/time/magazine/article/0,9171,817454,00.html. Retrieved 31 March 2010.
^ "Einstein in Princeton / Scientist, Humanitarian, Cultural Icon". Historical Society of Princeton. http://www.princetonhistory.org/museum_alberteinstein.cfm. Retrieved 31 March 2010.
^ The Case of the Scientist with a Pulsating Mass, 14 June 2002, http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/436253, retrieved 11 June 2007
^ Albert Einstein Archives (April 1955), "Draft of projected Telecast Israel Independence Day, April 1955 (last statement ever written)", Einstein Archives Online, http://www.alberteinstein.info/db/ViewImage.do?DocumentID=20078&Page=1, retrieved 14 March 2007
^ Cohen, J.R.; Graver, L.M. (November 1995), "The ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm of Albert Einstein", Surgery, Gynecology & Obstetrics 170 (5): 455–8, PMID 2183375.
^ O'Connor, J.J.; Robertson, E.F. (1997), "Albert Einstein", The MacTutor History of Mathematics archive, School of Mathematics and Statistics, University of St. Andrews, http://www-history.mcs.st-andrews.ac.uk/Biographies/Einstein.html, retrieved 14 March 2007
^ Dr. Albert Einstein Dies in Sleep at 76. World Mourns Loss of Great Scientist., New York Times, 19 April 1955, "Princeton, New Jersey, 18 April 1955. Dr. Albert Einstein, one of the great thinkers of the ages, died in his sleep here early today."
^ The Long, Strange Journey of Einstein's Brain, National Public Radio, http://www.npr.org/templates/story/story.php?storyId=4602913, retrieved 3 October 2007
^ a b "Einstein archive at the Instituut-Lorentz". Instituut-Lorentz. 2005. Retrieved on 21 November 2005.
^ a b Hans-Josef Kuepper. "List of Scientific Publications of Albert Einstein". Einstein-website.de. http://www.einstein-website.de/z_physics/wisspub-e.html. Retrieved 2011-04-03.
^ (Einstein 1905d)
^ Hawking, S. W. (2001), The Universe in short, Bantam Books, ISBN 0-55-380202-X
^ Schwartz, J.; McGuinness, M. (1979), Einstein for Beginners, Pantheon Books, ISBN 0-39-450588-3
^ (Einstein 1905e)
^ For a discussion of the reception of relativity theory around the world, and the different controversies it encountered, see the articles in Thomas F. Glick, ed., The Comparative Reception of Relativity (Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1987), ISBN 9027724989.
^ Pais, Abraham (1982), Subtle is the Lord. The Science and the Life of Albert Einstein, Oxford University Press, pp. 382–386, ISBN 019853907X
^ Einstein, Albert (1905), "Über einen die Erzeugung und Verwandlung des Lichtes betreffenden heuristischen Gesichtspunkt", Annalen der Physik 17: 132–148, Bibcode 1905AnP...322..132E, doi:10.1002/andp.19053220607, http://www.zbp.univie.ac.at/dokumente/einstein1.pdf, retrieved 27 June 2009
^ (Einstein 1905a).
^ http://www.osti.gov/accomplishments/nuggets/einstein/solidcolda.html Celebrating Einstein "Solid Cold". U.S. DOE. Office of Scientific and Technical Information. 2011.
^ Pais, Abraham (1982), Subtle is the Lord. The Science and the Life of Albert Einstein, Oxford University Press, p. 522, ISBN 019853907X
^ Levenson, Thomas. "Einstein's Big Idea". Public Broadcasting Service. 2005. Retrieved on 25 February 2006.
^ Albert Einstein, Nobel lecture in 1921
^ van Dongen, Jeroen (2010) Einstein's Unification Cambridge University Press, p.23.
^ (Einstein 1917a)
^ (Einstein 1917b)
^ (Einstein 1924)
^ Cornell and Wieman Share 2001 Nobel Prize in Physics, 9 October 2001, http://www.nist.gov/public_affairs/releases/n01-04.htm, retrieved 11 June 2007
^ (Einstein 1950)
^ Miller, Arthur I. (1981). Albert Einstein's special theory of relativity. Emergence (1905) and early interpretation (1905–1911). Reading: Addison–Wesley. pp. 325–331. ISBN 0-201-04679-2.
^ Wright, Karen (30 September 2004). "The Master's Mistakes". Discover Magazine. http://discovermagazine.com/2004/sep/the-masters-mistakes/article_view?b_start:int=1&-C=. Retrieved 15 October 2009.
^ Moore, Walter (1989), Schrödinger: Life and Thought, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-43767-9
^ Goettling, Gary. Einstein's refrigerator Georgia Tech Alumni Magazine. 1998. Retrieved on 21 November 2005. Leó Szilárd, a Hungarian physicist who later worked on the Manhattan Project, is credited with the discovery of the chain reaction
^ In September 2008 it was reported that Malcolm McCulloch of Oxford University was heading a three-year project to develop more robust appliances that could be used in locales lacking electricity, and that his team had completed a prototype Einstein refrigerator. He was quoted as saying that improving the design and changing the types of gases used might allow the design's efficiency to be quadrupled.Alok, Jha (21 September 2008), Einstein fridge design can help global cooling, London: The Guardian, http://www.guardian.co.uk/science/2008/sep/21/scienceofclimatechange.climatechange, retrieved 22 February 2011
^ (Einstein 1969). A reprint of this book was published by Edition Erbrich in 1982, ISBN 388682005X
^ (Einstein 1935)
^ Aspect, Alain; Dalibard, Jean; Roger, Gérard (1982). "Experimental test of Bell's inequalities using time-varying analyzers". Physical Review Letters 49 (25): 1804–1807. Bibcode 1982PhRvL..49.1804A. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.49.1804. The first of many experimental tests relating to EPR.
^ "Obituary". New York Times. 1986-07-12. http://query.nytimes.com/gst/fullpage.html?res=9A0DEFD9153FF931A25754C0A960948260. Retrieved 2011-04-03.
^ "Letters Reveal Einstein Love Life", BBC News (BBC), 11 July 2006, http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/5168002.stm, retrieved 14 March 2007
^ Roger Richman Agency (2007), "Albert Einstein Licensing", http://www.albert-einstein.net/index2.html, retrieved 25 March 2007 [dead link]; Archive copy at the Wayback Machine.
^ Einstein, Corbis Rights Representation, http://einstein.biz/, retrieved 8 August 2008
^ The New Yorker April 1939 pg 69 Disguise
^ [2] Einstein's Dream for orchestra by Cindy McTee
^ a b Golden, Frederic (3 January 2000), "Person of the Century: Albert Einstein", Time, http://www.time.com/time/time100/poc/magazine/albert_einstein5a.html, retrieved 25 February 2006
^ Albert Einstein – Frequently Asked Questions, Nobelprize.org, 18 April 1955, http://nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/physics/laureates/1921/einstein-faq.html, retrieved 7 January 2009
^ Einstein Collected Papers, Vol. 8, doc. 562
^ BBC (11 July 2006), "Letters Reveal Einstein Love Life", BBC News (BBC), http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/5168002.stm, retrieved 25 November 2008
^ MSNBC Report 10 July 2006 [3]
^ a b Marco Mamone Capria (2005) Physics before and after Einstein p.5. IOS Press, 2005
^ World Year of Physics 2005, http://www.wyp2005.org/overview.html, retrieved 3 October 2007
^ Brunhouse, Jay (2008) Maverick Guide to Berlin Pelican Publishing Company
^ Einsteinium and Fermium, http://pubs.acs.org/cen/80th/einsteiniumfermium.html, retrieved 6 June 2009
^ (PDF) History of the International Atomic Energy Agency – The First Forty Years, International Atomic Energy Agency, p. 30, ISBN 9201023979, http://www-pub.iaea.org/MTCD/publications/PDF/Pub1032_web.pdf, retrieved 6 June 2009
^ Spratt, Christopher E. (April 1990), "The Hungaria group of minor planets", Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada 84 (2): 123–131, Bibcode 1990JRASC..84..123S
^ Isaacson, Walter (3 January 2000), "Person of the Century: Why We Chose Einstein", Time, http://www.time.com/time/time100/poc/magazine/who_mattered_and_why4a.html, retrieved 16 July 2007
^ Howard, Don, and Stachel, John J. Einstein: The Formative Years, 1879–1909, p. 159, Springer (2000)
^ "Einstein the greatest". BBC News. 29 November 1999. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/541840.stm.
^ Mother Teresa Voted by American People as Most Admired Person of the Century, 31 December 1999, http://www.gallup.com/poll/3367/Mother-Teresa-Voted-American-People-Most-Admired-Person-Century.aspx, retrieved 13 August 2008
^ Walhalla, official guide booklet. p. 3. Translated by Helen Stellner and David Hiley, Bernhard Bosse Verlag Regensburg, 2002
^ (in German) Walhalla Ruhmes- und Ehrenhalle, http://www.walhalla-regensburg.de/deutsch/index.shtml, retrieved 3 October 2007
^ Biography of J. Schwinger from University of St Andrews, MacTutor History of Mathematics Archive (Last accessed 17 December 2006).
^ a b The Month at Caltech, April 1954 issue, p. 20 (Last accessed on 4 September 2007).
^ The Americana Annual 1962: An Encyclopedia of the Events of 1961, Americana Corporation, 1962, ISSN 0196-0180
^ Astronautics and Aeronautics, 1967, Scientific and Technical Information Branch, NASA, 1968, ISSN 0519-2366
^ Sigmund, Dawson, Muhlberger (2006), Kurt Godel: The Album, Wiesbaden: Vieweg, ISBN 3834801739
^ Albert Einstein Society in Bern retrieved 17 July 2010
^ Pugwash Online, http://www.pugwash.org/about/history.htm, retrieved 20 December 2009
Further reading
Fölsing, Albrecht (1997): Albert Einstein: A Biography. New York: Penguin Viking. (Translated and abridged from the German by Ewald Osers.)
Hoffmann, Banesh, with the collaboration of Helen Dukas (1972): Albert Einstein: Creator and Rebel. London: Hart-Davis, MacGibbon Ltd.
Isaacson, Walter (2007): Einstein: His Life and Universe. Simon & Schuster Paperbacks, New York. ISBN 9780743264730
Moring, Gary (2004): The complete idiot's guide to understanding Einstein ( 1st ed. 2000). Indianapolis IN: Alpha books (Macmillan USA). ISBN 0028631803
Pais, Abraham (1982): Subtle is the Lord: The science and the life of Albert Einstein. Oxford University Press. The definitive biography to date.
Pais, Abraham (1994): Einstein Lived Here. Oxford University Press.
Parker, Barry (2000): Einstein's Brainchild. Prometheus Books. A review of Einstein's career and accomplishments, written for the lay public.
Schweber, Sylvan S. (2008): Einstein and Oppenheimer: The Meaning of Genius. Harvard University Press. ISBN 978-0674028289.
Oppenheimer, J.R. (1971): "On Albert Einstein," p. 8-12 in Science and synthesis: an international colloquium organized by Unesco on the tenth anniversary of the death of Albert Einstein and Teilhard de Chardin, Springer-Verlag, 1971, 208 pp. (Lecture delivered at the UNESCO House in Paris on December 13, 1965.) Also published in The New York Review of Books, March 17, 1966, On Albert Einstein by Robert Oppenheimer
External links
Find more about Albert Einstein on Wikipedia's sister projects:
Definitions from Wiktionary
Images and media from Commons
Learning resources from Wikiversity
News stories from Wikinews
Quotations from Wikiquote
Source texts from Wikisource
Textbooks from Wikibooks
Works by Albert Einstein (public domain in Canada)
The MacTutor History of Mathematics archive, School of Mathematics and Statistics, University of St Andrews, Scotland, April 1997, http://www-history.mcs.st-andrews.ac.uk/Biographies/Einstein.html, retrieved 14 June 2009
Why Socialism? by Albert Einstein, Monthly Review, May 1949
Nobelprize.org Biography:Albert Einstein
The Einstein You Never Knew - slideshow by Life magazine
Albert Einstein--Watch Videos
Science Odyssey People And Discoveries
MIT OpenCourseWare STS.042J / 8.225J : Einstein, Oppenheimer, Feynman: Physics in the 20th Century Free, independent study course that explores the changing roles of physics and physicists during the 20th century.














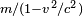 as the expression for the
as the expression for the 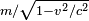 for the transverse mass. As Miller points out, this is equivalent to the transverse mass predictions of both Einstein and Lorentz. Einstein had commented already in the 1905 paper that "With a different definition of force and acceleration, we should naturally obtain other expressions for the masses. This shows that in comparing different theories... we must proceed very cautiously."
for the transverse mass. As Miller points out, this is equivalent to the transverse mass predictions of both Einstein and Lorentz. Einstein had commented already in the 1905 paper that "With a different definition of force and acceleration, we should naturally obtain other expressions for the masses. This shows that in comparing different theories... we must proceed very cautiously."



